
- Altmetric
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Structural elements of the SFKs and mechanisms of kinase regulation
- 3 Cysteine residues in the SH2 domain
- 4 Cysteines residues in the kinase domain
- 5 Cysteines in the unique domains
- 6 Polymorph diversity of cysteine structure and reactivity
- 7 Functional consequences of cysteine oxidation in kinase regulation
- 8 Implications for covalent drug development
- 9 Conclusions
- Declaration of competing interest
The Src Family Kinases (SFKs) are pivotal regulators of cellular signal transduction and highly sought-after targets in drug discovery. Their actions within cells are controlled by alterations in protein phosphorylation that switch the SFKs from autoinhibited to active states. The SFKs are also well recognized to contain redox-active cysteine residues where oxidation of certain residues directly contribute to kinase function. To more completely understand the factors that influence cysteine oxidation within the SFKs, a review is presented of the local structural environments surrounding SFK cysteine residues compared to their quantified oxidation in vivo from the Oximouse database. Generally, cysteine local structure and degree of redox sensitivity vary with respect to sequence conservation. Cysteine residues found in conserved positions are more mildly redox-active as they are found in hydrophobic environments and not fully exposed to solvent. Non-conserved redox-active cysteines are generally the most reactive with direct solvent access and/or in hydrophilic environments. Results from this analysis motivate future efforts to conduct comprehensive proteome-wide analysis of redox-sensitivity, conservation, and local structural environments of proteins containing reactive cysteine residues.
Introduction
Revealing the nature of the Src non-receptor tyrosine (Tyr) kinase has fundamentally transformed biology and medicine[1,2]. The discovery of the Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) revolutionized cancer biology as the earliest defined virus responsible for the transmission of cancer[3], and due to the fact that RSV contained single-stranded RNA lead to fundamental understandings of retroviruses as well as the discovery of reverse transcription[4]. The astonishing correspondence of the viral Src gene as comparted to the cellular Src gene in healthy tissues ushered in a new era in cancer biology with Src defined as the first proto-oncogene, a bedrock concept at the center of modern oncology[5,6]. Finally, combined molecular and cellular biological research divulged that the Src kinase uniquely phosphorylates the Tyr amino acid, instead of Ser/Thr, establishing the class of protein Tyr kinases[7]. The Src kinase is now widely recognized as the prototypical member of a family of non-receptor Tyr kinases that harbors its namesake, namely the Src family kinases (SFKs), which conduct intracellular signal transduction processes in various biological contexts[8], and structure-based studies have revealed the nature of their exquisite activating mechanisms[9,10].
Physiological processes are diversely regulated in tissues often by local post-translational modifications (PTMs) of signaling proteins, such as protein phosphorylation[11]. It is well appreciated that a major mode of such occurs from the well-controlled generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in tissues that induce PTMs of redox-sensitive cysteine residues in protein targets that directly impact protein structure and function[12,13]. As significant regulators of cellular signal transduction, recent studies have sought to address the relevance of ROS-promoted cysteine oxidation in the context of protein Tyr kinase regulation, including the SFKs[[14], [15], [16], [17]]. A routine survey of sequences reveals that a variety of cysteine residues are found throughout the SFKs with varying degrees of conservation, and many studies have sought to address their susceptibility to oxidation and subsequent impacts on regulation[[18], [19], [20], [21], [22], [23], [24]]. The recent release of a proteomics database (Oximouse) [25] by Chouchani and co-workers has revolutionized our understanding of thiol-based redox-signaling enabling the comprehensive and quantitative mapping of protein cysteine oxidation in vivo [26].
The sulfur-containing cysteine amino acid is uniquely reactive among amino acids and often critical for protein structure and function. Generally, the conjugate-base cysteine thiolate anion (Cys-S-) is the most relevant reactive form that can be accessible through acid-base equilibration from the cysteine thiol (Cys-SH)[27,28]. However, not all cysteine residues are reactive and exhibit a variable range of Cys-SH pKa found across the proteome[29,30]. While rationalizations are used to justify cysteine reactivity, such as local electrostatics and accessibility to solvent[26,28,31], a detailed understanding of the structural factors that influence cysteine oxidation is lacking thereby motivating efforts to more completely survey cysteine reactivity in protein families containing diverse redox-active cysteines.
In this review, a systematic survey of each SFK cysteine is presented with respect to conservation within the SFKs, local structural environment, and percent oxidation from Oximouse[32]. Overall trends appear to indicate that fully conserved cysteine residues appear more mildly redox-sensitive compared to non-conserved unique cysteine residues. Implications of these findings for regulation and covalent drug development are discussed.
Structural elements of the SFKs and mechanisms of kinase regulation
Definition of autoinhibited and active states from X-ray crystallography
The SFKs possess a conserved motif of structured domains that permit control of their Tyr kinase activity. Structural elucidation with X-ray crystallography of c-Src [33,34] and HCK [35,36] generated the first snapshots of the autoinhibited state. A consensus activation mechanism based on these structures indicates that SFK activation proceeds via unlatching of the autoinhibited complex clamped into this conformation by phosphorylation at Tyr-527 on the C-terminal tail[9,37], which is regulated by activity of the C-terminal Src kinase (CSK) (Fig. 1A and B)[38]. The intramolecular domain-domain interactions maintain the kinase domain in the inactive configuration. Release of these interactions is accomplished through a combination of events that can involve SH3 competitive binding of poly-proline motifs in peptides[39], dephosphorylation of pTyr-527, and/or competition with a tighter binding pTyr-containing peptide fragment (Fig. 1C). “Unclamping” of the SH2 and SH3 domains alleviate the autoinhibiting constraints from the “back” of the kinase domain allowing for structural flexibility to convert to the active state (Fig. 1D)[37,40]. The most important structural changes involve unfolding of the kinase A-loop (orange), which exposes Tyr-416 for autophosphorylation [34] and the resulting phosphorylated tyrosine facilitates permanent A-loop unfolding, accessibility of substrates to the ATP site for phosphoryl transfer, and inward rotation of the ɑC-helix (red)[41]. In more detail, the folded A-loop (orange in Fig. 1E) holds back the ɑC-helix in the inactive conformation and Glu-310 is positioned toward solvent. Upon A-loop unfolding, promoted by breaking the SH2 and SH3 domain-domain interactions, the ɑC-helix has the open space to rotate inward establishing the activating salt bridge between Lys-295 and Glu-310 (Fig. 1F). These insights from crystal structures of Src and other SFKs indicate that their activation is complex involving large-scale conformational changes mediated through intramolecular domain-domain interactions and changes in phosphorylation of pertinent tyrosine residues[9]. Understanding the nature of these 3-dimensional SFK structures are critical when discussing the potential roles of reactive cysteine residues and rationalizing their susceptibility to oxidation.

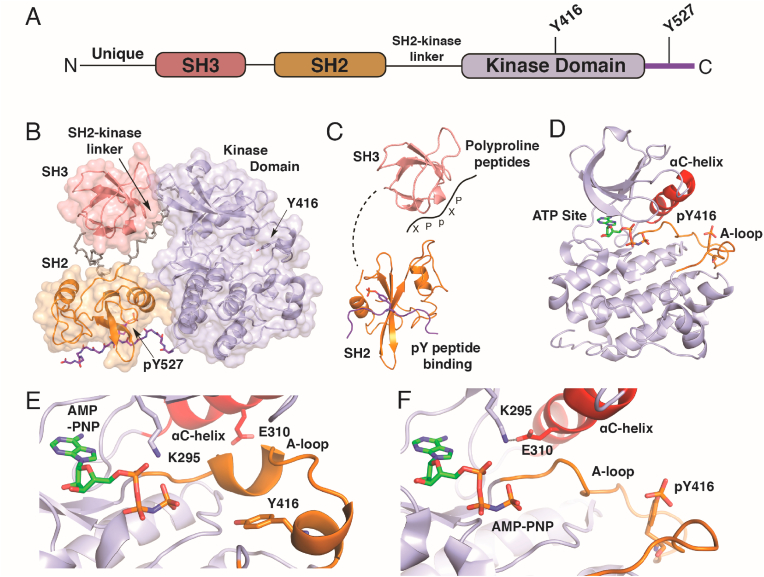
Structural basis for activation of the non-receptor Src family kinases from X-ray crystallography. A) The sequence of all SFKs contain a “Src module” consisting of consecutive encoding of structured SH3, SH2, and a kinase domains following a unique sequence in each SFK. Generally, two regulatory tyrosines (Y416 and Y527 in the chicken Src sequence numbers) serve as targets of phosphorylation & dephosphorylation. B) The Autoinhibited (closed) structure of Src (PDB code 2SRC) contains the Src module folded into a compact structure with SH2 an SH3 domains maintaining the kinase domain in the inactive conformation dependent on dephosphorylation at Y416 and phosphorylation at 527. C) Activation of Src is multifaceted and can proceed via any combination of engagement of SH2 with phosphopeptides, competition of the SH2-kinase linker with exogenous polyproline peptide motifs (-XPpXP-), and dephosphorylation at pY527. D) Structure of the active kinase domain containing unfolded, phosphorylated A-loop (pY416) and inward rotated αC-helix (PDB ID 3DQW). E) View of catalytic cleft of autoinhibited versus (PDB ID 2SRC)) and F) active Src (PDB ID 3DQW) showing the structural consequences of A-loop unfolding and the formation of the Lys-295 to Glu-310 H-bond via inward rotation of the αC-helix.
Characterizing the intermediates of SFK activation from computational modeling
As X-ray crystal structures represent distinct states, more detailed understanding has been afforded by computational modeling of Src with molecular dynamics (MD) simulations specifically motivated to elucidate the intermediate structures along the trajectory of activation and expose their vulnerability to inhibition for drug discovery[[41], [42], [43], [44]]. Results from such MD simulations indicate that the isolated Src kinase domain undergoes transition from inactive to active states through two key intermediates that involve first transitional unfolding of the A-loop (I1) followed by partial rotation inward ɑC-helix (I2)[42]. These findings indicate that the late-stage ɑC-helix inward rotation is ultimately most consequential for SFK activity as compared to the A-loop unfolding[42]. Further work indicates that the A-loop is considerably flexible while Y416 is unphosphorylated where the kinase can sample the active state, however only transiently[44]. Upon phosphorylation, pY416 alters the stability of the kinase and locks it into the active state that is catalytically active and consistent with structures presented previously (Fig. 1)[44]. Overall, these findings are consistent with a stepwise conversion of Src from the inactive autoinhibited state first into an “active-like” state where the A-loop is unfolded but not yet phosphorylated. While unfolded, the A-loop is exposed and can be transphosphorylated to arrive at the fully active state allowing for inward ɑC-helix rotation (see Fig. 1E versus 1F). Subsequent experimental studies have reinforced this notion that several intermediates are accessed in the activation of the non-receptor tyrosine kinases through large-scale dynamic allosteric networks[45,46].
Biological insights into SFK activation through cell-based studies
The molecular-level details described above from X-ray crystallography and MD simulations are especially valuable when considering measurements from cell-based studies. SFK activation can be interrogated in cells with a number of techniques, such as blotting for phosphorylation status, but considerable insight into activation and resulting structural changes in cells has benefited from the development of FRET-based biosensors (e.g., Src [47], Fyn [48,49], Lck [[50], [51], [52]]), which allow for interrogation of SFKs in “opened” versus “closed” conformations and changes upon stimulation. Importantly, FRET-based biosensors are useful as they revealed properties otherwise hidden from biochemical settings, such as how certain Src inhibitors impact localization as well as stabilize "open" versus "closed" conformation in cellular settings [47]. While monitoring “closed” conformations of SFK appear to reflect autoinhibited or “latched/clamped” SFKs (Y416/pY517), the “open” conformation can represent a series of states depending on the intermediates accessible, as explained from MD simulations, in addition to the fully active pY416 "open" form. A key case that has been especially revealing is for the activation of Lck through T-cell receptor signaling[53]. Interestingly, resting T-cells have been found to contain 50% of Lck in an intermediate “primed” conformation where Tyr-416 and Tyr-527 (Tyr-394 and Tyr-505 in Lck sequence numbers) are not phosphorylated[54]. This “primed” state of Lck, however, appears to not be the active form as recent studies on Lck in T-cell activation demonstrated that phosphorylation at Lck pY416 is required to elicit full T-cell signaling[51,52]. This indicates that the “primed” form of Lck is presumably indistinguishable from the fully extended “open” conformation in FRET-based biosensor measurements[51], supporting the notion that “primed” Lck may be one of the intermediate states seen in MD simulations (I1/I2) that is not fully active with a partially unfolded A-loop[[41], [42], [43]]. Utilization of FRET-based SFK biosensors, to my knowledge, have yet to be applied to SFK redox-regulation and may offer key insights into the structural dynamics and cysteine oxidation in response to cellular stimuli.
In contrast, the situation pertaining to Fgr activation in cells appears uniquely atypical involving non-canonical activation independent of SH2 and SH3 “unclamping” potentially due to sequence differences in the SFK A-loops[55]. A non-conserved NPC-motif in the Fgr A-loop (the three amino acids immediately following Y416 where in all other SFKs these amino acids are conserved in a TAR-motif) is thought to be responsible for this idiosyncratic behavior, although further studies appear necessary to confirm this mechanism more fully[55]. These findings demonstrate the complicated nature of SFK activation in their particular cellular settings further motivating efforts to compare and contrast their activation mechanisms and the differences associateed with their redox-active cysteine residues.
Cysteine residues in the SH2 domain
SH2 domains are found within many human proteins (>100) and function as a versatile recognition domain for pTyr-containing proteins. The conserved fold of the SH2 domain consists of about 100 amino acids with two ɑ-helixes and seven β-sheets ordered in a βɑβββββɑβ pattern with a central anti-parallel β-sheet flanked by the two ɑ-helixes (Fig. 2, Fig. 3A)[56]. Cysteine residues are found at various positions within the SFK SH2 domains with varying degrees of sequence conservation (Fig. 3B, Table 1).

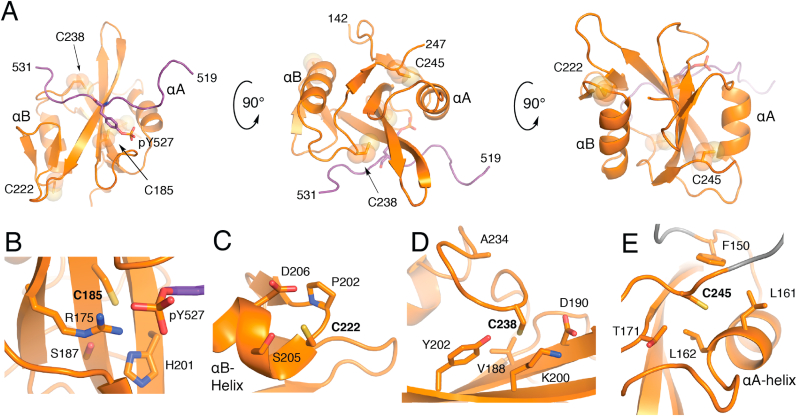
Structure of the SH2 Domain and CysteineStructuralEnvironments. A) Overall fold of the Src SH2 domain (orange) in complex with pTyr-527 C-terminal peptide (purple) from PDB ID 2SRC. Local structural environment for B) Cys-185, C) Cys-222 (visualized from LYN structure, PDB ID 4TZI), D) Cys-238, and E) Cys-245. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)

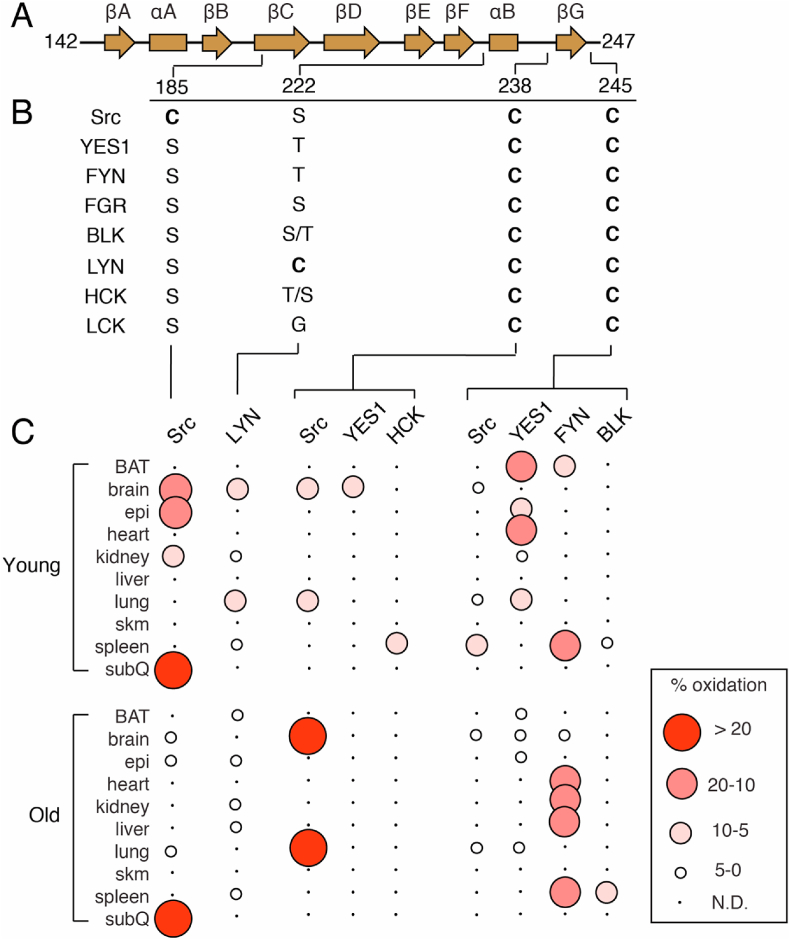
Sequence homology of cysteine residues of SFK SH2 domains and percent oxidation. A) Secondary structural elements of SFK SH2 domains and location of cysteine residues. B) Sequence homology of residues at positions of cysteine residues. Two residues are specified if there is a difference between human and mouse sequences. The right and left most residues correspond to human and mouse, respectively. C) Visualization of percent oxidation from Oximouse. Abbreviations (BAT, brown adipose tissue; epi, epididymal fat; sub Q, subcutaneous fat; skm, skeletal muscle; N.D., not detected).

| Src | Chicken | Cys-185 | Lys-206 | Ser-222 | Cys-238 | His-239 | Cys-245 |
| Human | Cys-188 | Lys-209 | Ser-225 | Cys-241 | His-242 | Cys-248 | |
| Mouse | Cys-193 | Lys-214 | Ser-230 | Cys-246 | His-247 | Cys-253 | |
| YES1 | |||||||
| Human | Ser-195 | Lys-216 | Thr-232 | Cys-248 | His-249 | Cys-255 | |
| Mouse | Ser-193 | Lys-214 | Thr-230 | Cys-246 | His-249 | Cys-253 | |
| FYN | |||||||
| Human | Ser-186 | Lys-207 | Thr-223 | Cys-239 | Cys-240 | Cys-246 | |
| Mouse | Ser-186 | Lys-207 | Thr-223 | Cys-239 | Cys-240 | Cys-246 | |
| FGR | |||||||
| Human | Ser-181 | Lys-202 | Ser-218 | Cys-234 | Asn-245 | Cys-240 | |
| Mouse | Ser-169 | Lys-190 | Ser-206 | Cys-222 | Asn-223 | Cys-228 | |
| BLK | |||||||
| Human | Ser-161 | Cys-181 | Ser-197 | Cys-213 | Gln-214 | Cys-220 | |
| Mouse | Ser-167 | Ser-175 | Thr-203 | Cys-219 | Gln-222 | Cys-226 | |
| LYN | |||||||
| Human | Ser-166 | Ser-187 | Cys-203 | Cys-219 | Arg-220 | Cys-226 | |
| Mouse | Ser-166 | Ser-187 | Cys-203 | Cys-219 | Arg-220 | Cys-226 | |
| HCK | |||||||
| Human | Ser-181 | Thr-202 | Thr-218 | Cys-234 | Gln-235 | Cys-241 | |
| Mouse | Ser-179 | Thr-200 | Ser-216 | Cys-232 | Gln-233 | Cys-239 | |
| LCK | |||||||
| Human | Ser-164 | Asn-185 | Gly-201 | Cys-217 | Thr-218 | Cys-234 | |
| Mouse | Ser-164 | Asn-185 | Gly-201 | Cys-217 | Thr-218 | Cys-234 | |
Cys-185
In the autoinhibited complex, the Src C-terminal tail binds to the central β-sheet, positioning the pTyr-527 moiety within a pocket near Cys-185 and other hydrophilic amino acid sidechains (Fig. 2B). Entirely unique to Src, Cys-185 is located on the βC-sheet in a position otherwise conserved as a serine, the hydrophilic alcohol analogue of Cys (Fig. 3)[57]. Of the residues within this region, the conserved cationic Arg-175, and to a lesser extent Arg-155, is principally responsible for binding pTyr-527 and also within H-bond distance of Cys-185[57,58]. Loss of pTyr-527 binding opens this region of the SH2 domain rendering Cys-185 accessible to solvent upon Src activation[59].
Based on the local structural environment around Cys-185, it is straightforward to rationalize how this residue is redox-active due to solvent accessibility and presence in a hydrophilic region including the cationic Arg-175 (Fig. 2B). Indeed, accumulated evidence from a variety of studies have shown that Cys-185 likely exhibits a low pKa near physiological pH[60], is shown to be involved in disulfide bonding with cortactin at Cys-112/246[61], and most recently readily oxidized by H2O2 to sulfenic acid that is involved in the activation of the Src kinase activity[21]. Correspondingly, Cys-185 was found to be highly oxidized (>20%) in the Oximouse database of which was observed predominantly in the subcutaneous fat and elevated with age (Fig. 3C)[26]. Notably, of all SFKs cysteine residues analyzed in oximouse, Cys-185 represents the most highly oxidized cysteine (>50% in old mice subQ).
Cys-222
Another rare Cys found in a single SFK is Cys-203 in LYN (222 in avian Src, Fig. 2C). This solvent exposed residue located on a short loop connecting βF and ɑB-helix on the opposite of the domain from the pTyr binding site (Fig. 2C). This cysteine is found oxidized in Oximouse generally more so in the younger mouse. While LYN is recognized to be redox-active [62,63], this specific residue has not been addressed previously. It is noteworthy that both Cys-185 and Cys-222 are unique in their respective SFK in positions that mostly contain hydrophilic Ser or Thr residues.
Cys-238 and Cys-245
The two completely conserved cysteine residues in the SH2 domain are located near the C-terminus (Fig. 2D and E), and a sequence alignment of reveals a conserved (D/A)GLCXXLXXXCX motif[64]. Structurally, both of these residues are on flexible loops that bookend the βG-sheet, and are generally accessible by solvent. Crystal structure coordinates indicate that both residue side chains point away from solvent, and the major difference between these residues is the local proximity of hydrophilic versus hydrophobic residues in the case of Cys-238 and Cys-245, respectively. Oxidation of these residues is observed in Oximouse, but only in a subset of SFKs (Fig. 3). Relative percent oxidation indicates that Src is more oxidized at Cys-238 both in the brain and lung, but is considerably higher in older mice compared to young, while on the other hand, Src Cys-245 is oxidized within the brain and lung, but at lower levels compared to YES1 and FYN in young and old mice, respectively.
Cysteines residues in the kinase domain
Cysteine residues are found in a variety of kinases and have been studied in the context of redox-dependent signaling [16,65,66] as well as explored extensively in efforts to develop cysteine-targeting inhibitors as covalent inhibitors [[67], [68], [69], [70]]. Various covalent inhibitor development efforts have been directed against SFKs, with emphasis on targeting rare cysteines to direct specificity for a given SFK family member, a persistent challenge in developing clinically viable inhibitors[71,72]. The kinase domain (also referred to as the catalytic domain) contains a number of redox-active cysteines with variable degrees of conservation (Table 2).

| Src | Chicken | Cys-277 | Ser-342 | Ser-345 | Val-399 | Cys-400 | Arg-419 | Arg-438 | Cys-483 | Cys-487 | Cys-496 | Cys-498 |
| Human | Cys-280 | Ser-345 | Ser-348 | Val-402 | Cys-403 | Arg-422 | Arg-442 | Cys-486 | Cys-490 | Cys-499 | Cys-501 | |
| Mouse | Cys-285 | Asn-350 | Ser-353 | Val-407 | Cys-408 | Arg-427 | Arg-447 | Cys-491 | Cys-495 | Cys-504 | Cys-506 | |
| YES1 | Human | Cys-287 | Ser-352 | Ser-355 | Val-409 | Cys-410 | Arg-427 | Arg-446 | Cys-493 | Cys-497 | Asn-506 | Cys-508 |
| Mouse | Cys-285 | Ser-350 | Ser-353 | Ile-407 | Cys-408 | Arg-425 | Arg-444 | Cys-491 | Cys-495 | Asn-504 | Cys-506 | |
| FYN | Human | Gln-281 | Asn-346 | Ser-349 | Ile-403 | Cys-404 | Arg-423 | Arg-442 | Cys-487 | Cys-491 | Ile-500 | Cys-502 |
| Mouse | Gln-281 | Ser-346 | Ser-349 | Ile-403 | Cys-404 | Arg-423 | Arg-442 | Cys-487 | Cys-491 | Ile-500 | Cys-502 | |
| FGR | Human | Cys-273 | Cys-338 | Ser-341 | Ala-395 | Cys-396 | Cys-415 | Arg-434 | Cys-479 | Cys-483 | Glu-492 | Thr-494 |
| Mouse | Cys-261 | Cys-326 | Ser-329 | Ile-383 | Cys-384 | Gln-403 | Arg-422 | Cys-467 | Cys-471 | Glu-480 | Ala-482 | |
| BLK | Human | Gln-251 | Ala-316 | Cys-319 | Cys-373 | Cys-374 | Gln-393 | Val-411 | Arg-456 | Cys-460 | Ala-470 | Cys-472 |
| Mouse | Gln-245 | Ala-310 | Cys-313 | Cys-367 | Cys-368 | Gln-386 | Val-405 | Cys-450 | Cys-454 | Thr-464 | Cys-466 | |
| LYN | Human | Gln-257 | Ala-323 | Ser-326 | Met-380 | Cys-381 | Arg-400 | Cys-419 | Arg-464 | Cys-468 | Lys-477 | Cys-479 |
| Mouse | Gln-257 | Ala-323 | Ser-326 | Met-380 | Cys-381 | Arg-400 | Cys-419 | Arg-464 | Cys-468 | Lys-477 | Cys-479 | |
| HCK | Human | Gln-272 | Ala-337 | Ser-340 | Val-394 | Cys-395 | Arg-414 | Ser-433 | Arg-478 | Cys-482 | Met-491 | Cys-493 |
| Mouse | Gln-270 | Ala-335 | Ser-338 | Val-392 | Cys-393 | Arg-412 | Ser-431 | Arg-476 | Cys-480 | Ile-489 | Cys-491 | |
| LCK | Human | Gln-255 | Glu-320 | Ser-323 | Ser-377 | Cys-378 | Arg-397 | Thr-416 | Arg-461 | Cys-465 | Arg-474 | Cys-476 |
| Mouse | Gln-255 | Glu-320 | Ser-323 | Ser-377 | Cys-378 | Arg-397 | Thr-416 | Arg-461 | Cys-465 | Met-474 | Cys-476 | |
Cys-277 (P-loop)
The N-lobe of the kinase (260–338) contains a single cysteine located on the P-loop (or G-rich loop) that connects β1 and β2 (Fig. 4B). This position is a Cys in a minority of SFKs while otherwise conserved as a Gln (Fig. 5B). Fully exposed to solvent, Cys-277 has been the target of various covalent inhibitors of Src, YES, FGR[71,73], in addition to being the focus of the redox-regulation of Src[21,74,75]. In the later context, oxidation of Cys-277 to a sulfenic acid is uniquely positioned opposite the folded A-loop in the autoinhibited structure, and oxidation to a sulfenic acid promotes the opening of this loop in the redox-regulation of Src[21]. The Oximouse database indicates some levels of oxidation at Cys-277 in both Src and YES1, which is enhanced with age.

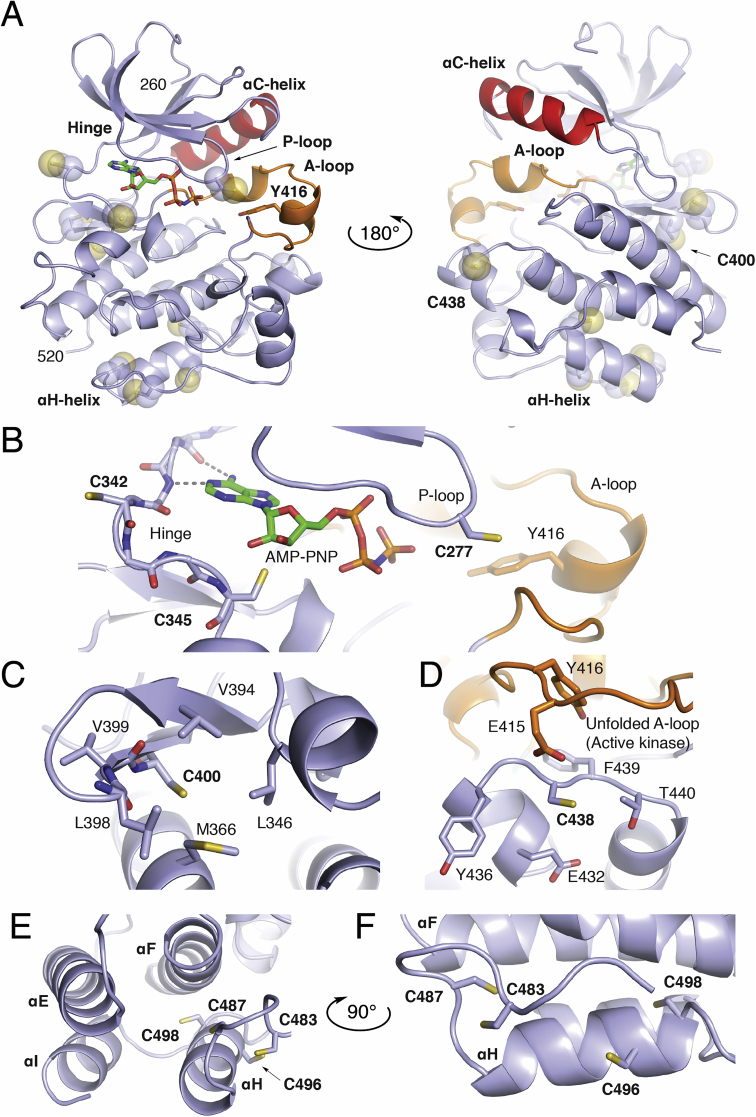
Structure of the Src Kinase Domain and CysteineStructuralEnvironments. A) Overall fold of the Src kinase domain (light blue), ɑC-helix (red), A-loop (orange) in complex with AMP-PNP defining the ATP-binding site from PDB ID 2SRC. Local structural environment for B) Cys-277, Cys-342, and Cys-345 near the ATP binding site and folded A-loop. C) Local hydrophobic residues around Cys-400. D) Placement of Cys-438 near hydrophilic residues, Tyr-416, and Glu-415 of the A-loop in the active kinase (PDB ID 1Y57). E) and F) Organization of the Cys-483, Cys-487, Cys-496, and Cys-498 cluster located near the C-terminal ɑH-helix. In cases where Cys residues are not present in the 2SRC kinase domain, the corresponding position has been mutated to a cysteine in PyMol. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)

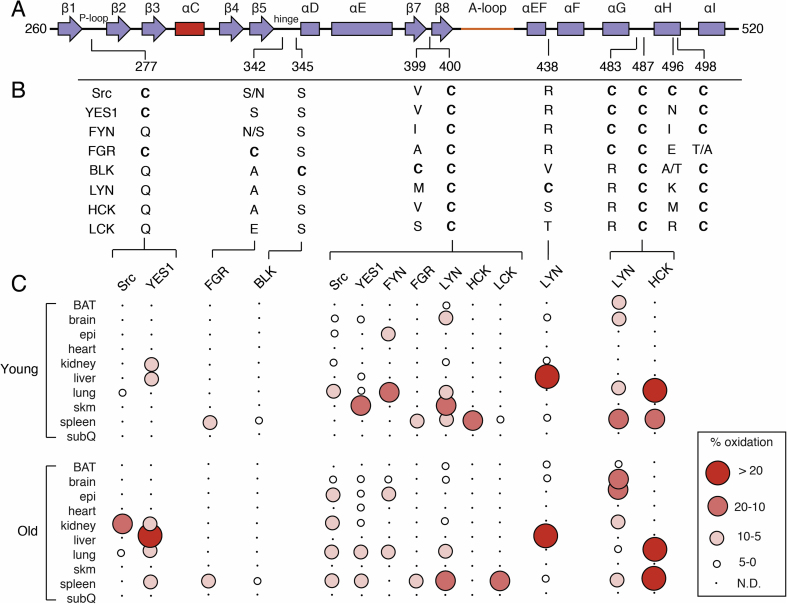
Sequence homology of cysteine residues of SFK kinase domains and percent oxidation. A) Secondary structural elements of SFK kinase domains and location of cysteine residues (colors consistent with Fig. 4). B) Sequence homology of residues at positions of cysteine residues. Two residues are specified if there is a difference between human and mouse sequences. The right and left most residues corresponds to human and mouse, respectively. C) Visualization of percent oxidation from Oximouse. Abbreviations (BAT, brown adipose tissue; epi, epididymal fat; subQ, subcutaneous fat; skm, skeletal muscle; N.D., not detected). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
Cys-342 & Cys-345 (Hinge region & front pocket)
Two non-conserved cysteine residues reside on the hinge region. Cys-342 of FGR is nearest the ATP binding site and the side chain points away from the catalytic binding site into solvent (Fig. 4B). Redox activity of FGR cysteines has yet to be explored, to my knowledge, but is found oxidized in the Oximouse. This position in the other SFKs is a mixture of hydrophilic and hydrophobic amino acids. On the other hand, Cys-345 of BLK is also located on the kinase hinge region near the ATP binding site, otherwise known as the front pocket position. This position of BLK, otherwise a conserved Ser, has also been unexplored previously and is structurally-related to the position of Cys-797 of EGFR [65,66], which is the target of clinically approved TKIs in cancer[76]. Oximouse shows low levels of oxidation of this residue are found in the mouse spleen.
Cys-400
Located on the β8-helix, directly below the catalytic cleft, Cys-400 is a completely conserved cysteine residue within the SFKs (Fig. 4C), and according to the Oximouse database, this residue is observed oxidized in nearly all SFKs (Fig. 5). Somewhat puzzlingly, the local structure around Cys-400 does not exhibit the typical structural elements of a reactive cysteine residue. Specifically, the region of the kinase domain where Cys-400 is located is structurally ridged, comparing active and inactive structures, in addition to being mostly obscured away from solvent and surrounded by hydrophobic residues. The potential impacts of oxidation on kinase function are also unclear as this location within the kinase domain is far from regulatory segments or domain-domain interactions[45,46]. Biochemical studies are necessary to more completely understand the apparent redox sensitivity of this highly conserved cysteine residue within the SFKs, especially motivated by its universal oxidation in vivo.
Cys-438
Unique to LYN, Cys-438 is located on a solvent exposed loop in between the ɑEF-helix and ɑF-helix within the vicinity of hydrophilic residues (Fig. 4D). Strikingly, this residue is found highly oxidized in the liver, and previously uncharacterized reactive LYN cysteine[62,63]. The location of this redox-active cysteine is especially intriguing due to its proximity to the unfolded A-loop of the active state[59]. Although potential interactions with anionic Glu-415 may dampen some reactivity of Cys-438, the impact of this unique cysteine on LYN activity may very well be important for kinase activation.
Cys-483, Cys-487, Cys-496, and Cys-498
A cluster of cysteine residues occurs near the C-terminus of the C-lobe that have garnered considerable attention for their potential roles in SFK redox regulation[16,17]. Cys-498 is conserved in all SFKs and present in >95% of protein Tyr kinases within a MXXCW motif[77]. Cys-487 is also highly conserved present in an extended CXXXXXXXMXXCW motif in 80% of protein Tyr kinases[77]. Two cysteines are also found in this cluster, Cys-483 and Cys-496, which are less conserved. Structurally, this cluster of residues decorates the base of the C-lobe around the ɑH-helix (Fig. 4E and F). Cys-483 and Cys-487 on the loop preceding the ɑH-helix are generally solvent exposed. Cys-496 on the ɑH-helix, and unique to Src, is on a turn of the helix that points the side chain into solvent, whereas Cys-498 is positioned within the four-helix bundle completely obscured from solvent. These cysteine residues occur in a structured region and the conservation of these residues has lead to proposals for their involvement in structural and functional roles across protein Tyr kinases[15,[78], [79], [80]]. However, despite evidence for their oxidation, the impact of these cysteines on SFK function remains unclear (Table 3). One indication may come from a recent study of Src solution dynamics that suggests the conserved Gly-449 on the ɑE-Helix directly across from Cys-498 is necessary for Src activation implying that structural changes to these cysteine residues may impact kinase domain dynamics[46]. Indeed, studies of SFK activation by HgCl2 and S-nitrosylation appear to react with cysteines in this motif[63,81]. Despite this degree attention paid to these cysteines in the SFKs with respect to redox regulation, very little oxidation is observed in this cluster in the Oximouse database. Oximouse detects significant degrees of oxidation at Cys-487 in LYN and HCK while other forms of oxidation in other SFKs at these residues are not detected. This apparent disparity between Oximouse and the literature highlight current needs with respect to sorting out the importance of the cysteine residues within this C-terminal region of the SFK kinase domain.

| Cysteine Residue1 | Modification (Functional Outcome) | Tissue Location of Oxidized Cysteine in Oximouse [26]2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Young Mice | Old Mice | |||
| Src | Cys-185 | Disulfide (Cortactin Binding) [61] | Brain, Epi, Kidney, subQ | Brain, Epi, Lung, subQ |
| Sulfenic Acid (Activating) [21] | ||||
| Cys-238 | NR | Brain, Lung | Brain, Lung | |
| Cys-245 | Proposed Disulfide (Activating) [92] | Brain, Lung, Spleen | Brain, Lung | |
| ND (Activating) [75] | ||||
| Cys-277 | Sulfenic Acid (Activating) [21] | Lung | Kidney, Lung | |
| Disulfide (Inactivating) [74] | ||||
| Cys-400 | NR | Brain, Epi, Kidney, Lung | Brain, Epi, Kindey, Lung, Spleen | |
| Cys-483 | ND (Activating) [93] | Not detected | Not detected | |
| Cys-487 | ND (Activating) [75,93,94] | Not detected | Not detected | |
| Disulfide (Activating) [92] | ||||
| Cys-496 | ND (Activating) [93] | Not detected | Not detected | |
| Cys-498 | ND (Activating) [75,93] S-nitrosylation (Activating) [81] | Not detected | Not detected | |
| Non-identified | ND (Activating) [95,96] | |||
| Sulfenic Acid (Activating) [87,97] | ||||
| S-glutathionylation (Activating) [87] | ||||
| YES1 | Cys-238 | NR | Brain | Not detected |
| Cys-245 | NR | BAT, Epi, Heart, Kidney, Lung | BAT, Brain, Epi, Lung | |
| Cys-277 | NR | Kidney, Liver | Kidney, Liver, Lung, Spleen | |
| Cys-400 | NR | Brain, Liver, Lung, skm | Brain, Epi, Heart, Lung, Spleen | |
| FYN | Cys-245 | NR | Brain, Spleen | Brain, Heart, Kidney, Liver, Spleen |
| Cys-400 | NR | Epi, Lung | Brain, Epi, Lung | |
| Cys-487 | ND (Activating) [98] | Not detected | Not detected | |
| Not specified | Sulfenic Acid (Activating) [99] | |||
| FGR | Cys-342 | NR | Spleen | Spleen |
| BLK | Cys-345 | NR | Spleen | Spleen |
| LYN | Cys-222 | NR | Brain, Kidney, Lung, Spleen | BAT, Epi, Kidney, Liver, Spleen |
| Cys-400 | NR | BAT, Brain, Kidney, Lung, skm, Spleen | BAT, Epi, Kidney, Lung Spleen | |
| Cys-438 | NR | Brain, Kidney, Liver, Spleen | BAT, Brain, Liver, Spleen | |
| Cys-487 | ND (Activating) [62] | BAT, Brain, Lung, Spleen | Bat, Brain, Epi, Kidney, Lung, Spleen | |
| HCK | Cys-238 | NR | Spleen | Not detected |
| Cys-400 | NR | Spleen | Not detected | |
| Cys-487 | NR | Lung, Spleen | Lung, Spleen | |
| Not specified | ND (Activating) [100] | |||
| LCK | Cys-400 | NR | Spleen | Spleen |
| Cys-487 & Cys-498 | ND (Activating) [101] | Not detected | Not detected | |
Adapted and modified from Table 1 of ref [16]. 1Sequece numbers in this table are from chicken Src for consistency. 2Oximouse tissue abbreviations (BAT, brown adipose tissue; epi, epididymal fat; subQ, subcutaneous fat; skm, skeletal muscle). NR “None Reported” designates a specific cysteine residue where oxidation has not been addressed previously. ND “Not Determined” designates a cysteine where the referenced study does not determine the modification. A graphical representation of the Oximouse percent oxidations along with sequence conservation can be found in Fig. 3, Fig. 5.
Cysteines in the unique domains
The scope of this review and analysis is focused on the cysteine residues within the structured SFK SH2 and kinase domains. It should be noted that there is a unique N-terminal segment in each SFK, which is largely unstructured, allowing for tailored functions to the individual settings of each SFK (e.g., Ref. [82]). A well characterized example is the unique domain of LCK, which contains cysteine residues that bind a zinc ion critical for anchoring the LCK kinase to the C-terminal tail of CD4 and CD8ɑ to regulate T lymphocyte functions[83,84]. Little is known if they are susceptible to oxidation. The SFK protein sequences reveal cysteine residues in this region in various SFKs, and no oxidation in these regions are observed in Oximouse.
Polymorph diversity of cysteine structure and reactivity
This review has presented a direct comparison between the degree of redox sensitivity of particular cysteine residues and their structural environment for a well-studied family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases. Since the architecture of the SH2 and kinase domains are practically identical in the SFKs[9,10], an insightful association is the degree of cysteine residue conservation and extent of redox activity within the family. Although challenging to completely generalize, it is most meaningful to compare the completely conserved residues to the rare non-conserved cysteine residues.
There are several conserved cysteine residues in the SFKs, such as Cys-238, Cys-245, Cys-400, Cys-487, Cys-498. When surveying Oximouse, all but one of these residues is detected oxidized across most of the SFKs (Cys-400, Fig. 5), and the remaining residues are found oxidized in select cases. Structurally, these residues are located near exposed surfaces, but not directly accessible to solvent, and are predominantly surrounded by hydrophobic residues. A notable exception is Cys-238, which is located near negative and positive residue side chains (Fig. 2D). It is somewhat straightforward then to rationalize that generally milder redox sensitivity of conserved cysteines is due to their hydrophobic environments and relative occlusion from solvent. Such residues would certainly be redox sensitive and potentially more relevant for regulated processes where oxidants could be accumulated due to the activation of NADPH Oxidase enzymes or mitochondria in localized compartments within the cell[85].
On the other hand, a variety of non-conserved redox cysteines are found in the SFKs. Two notable examples are the highly oxidized Cys-185 in Src and Cys-438 in LYN. The SH2 domain Src Cys-185, otherwise completely conserved as a Ser in the other SFKs, is located at the pTyr-527 binding pocket, and previously described to be important for regulating Src activity [21] and disulfide bonding to cortactin[61]. Less is known at present about the direct consequences resulting from the oxidation of LYN Cys-438, which is located in a position otherwise conserved as a positive Arg or Ser/Thr residues. Structurally, a cysteine at this position is straightforwardly accessible to solvent, and is located near hydrophilic residues[26]. Perhaps a bit confounding is the observation that the unfolded A-loop, which anchors a conserved Glu-415 near Cys-438, would be expected to further suppress redox reactivity in the active state (Fig. 5D). Interestingly, comparing the sequences of amino acids present at the corresponding position of most non-conserved cysteines are strictly conserved as hydrophilic Ser or Thr residues at positions like Cys-185 & Cys-222 and also Arg for Cys-438. Since the local electrostatic surroundings of these regions in the SFK proteins are largely consistent between family members, this observation suggests that non-conserved redox-active cysteine residues are found in locations where alcohol-conatining and/or charged residues are well tolerated. As more studies are needed to confirm such an observation, it seems reasonable that pockets containing hydrophilic residues would be ideally suited to stabilize the charged intermediates that occur as a result of cysteine oxidation. Additionally, this analysis also shows that not all non-conserved cysteines in the SFKs are highly redox-active in a universal sense. Examples of such non-conserved residues are Cys-342 and Cys-345 that are minimally redox-active as well as Cys-483 where oxidation is not detected.
Functional consequences of cysteine oxidation in kinase regulation
An essential question worth considering when differentiating cysteine residues on the basis of their redox sensitivity is the potential outcomes to kinase function. A summary of reported redox-dependent modifications of SFK cysteine residues, their impact on function, and the tissue location of oxidized cysteine residues found in Oximouse is presented in Table 3. Since kinases are universally regulated through non-redox mechanisms, the presence of redox-active cysteine residues could, and likely do, elicit fundamentally distinct effects on kinase regulation, especially in the context of when a cysteine is non-conserved. While much on the subject of kinase redox-regulation has been reviewed previously[16,65], molecular level details of reversible oxidation of cysteines in EGFR [20,86,87] and Src [21] offer key evidence that cysteine oxidation alter local changes in protein structure that enhance kinase activity. Additionally, several recent studies indicate that redox-dependent signaling is an increasingly recognized mode of kinase regulation, such as Aurora A Ser/Thr kinases[88,89], Fructosamine-3-kinase[90], and a variety of redox-dependent processes resulting from EGF stimulation indicating that many cysteines oxidized downstream of EGFR activation are made solvent exposed only upon structural rearrangements[91].
In a global sense, it is important to notice that functional relevance of SFK cysteine oxidation has not been comprehensively explored. As shown in Table 3, a variety of SFK cysteines shown or proposed to be oxidized previously are not detected oxidized in Oximouse while several examples of cysteines shown to be oxidized in Oximouse have not been explored for their functional significance or relevant cysteine modification(s). This is, in part, due to the fact that percent oxidation of cysteines obtained from the Oximouse database do not take into account the types of redox-dependent PTMs or the overall redox status of the cysteine characterized[26]. Dissecting mechanisms of redox-dependent regulation of kinases as dependent on cysteine oxidation will require systematic and detail-oriented studies leveraging combinations of biochemical and cell-based studies, which potentially contain essential insights into unique functional elements involved in redox signaling as well as drug discovery efforts in physiological contexts of dysregulated oxidant production.
Implications for covalent drug development
The emergence of effective anticancer drugs targeting kinases operating via the formation of potency-enabling covalent bonds to reactive cysteine residues motivates efforts to assess the degree to which cysteine residues are reactive toward reactive electrophiles across the kinome[[68], [69], [70]]. In a general sense, a nucleophilic cysteine, which is ideally suited to be targeted by a drug molecule containing an electrophilic warhead is intuitively likely to be redox-active. For example, both EGFR Cys-797 [76,102] and Src Cys-277 [71,103,104] are sites where redox-active cysteines have been targeted by covalent inhibitors. While a series of definitive proteome-level studies comparing the sensitivity of cysteine residues to oxidants and drugs containing cysteine-targeting electrophiles has not been reported, it remains valuable to consider the potential translational applications of identifying reactive cysteines on the basis of their surrounding protein structure.
Conclusions
The reviewed SFK structures and reactivity findings from Oximouse have afforded a comprehensive analysis of redox-active cysteine residues within a well-characterized family of proteins. Such analyses of proteins that function independent of oxidation, but that contain redox-active cysteine residues, offer key molecular insights into the local structural effects that control the reactivity of reactive cysteines. Results from this survey do not support a “one-size-fits-all” paradigm to rationalizing redox-activity from protein structural elements of cysteine sites, and instead offer a few lessons regarding structure and conservation. Most interestingly, strictly conserved cysteine residues are generally not robustly found oxidized, and their local structural environments appear consistent with the picture that such residues are milder in terms of susceptibility to oxidation. Alternatively, non-conserved and unique occurrences of cysteine residues in locations that are usually conserved as a polar Ser, Thr, or Arg amino acid are most reactive in the SFKs. Future research dedicated to understanding the nature of the local electrostatic environments around reactive cysteines will further refine these observations, and offer more direct approaches to identify reactive cysteine residues as sites of biological oxidation as well as the development of highly efficacious covalent drugs.
Declaration of competing interest
None.
References
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
Acknowledgements
This review is dedicated to my postdoctoral mentor Dr. Albert van der Vliet of the University of Vermont for his valuable mentoring in redox biology and first introducing me to protein kinases. This review benefited from input and helpful discussions from Dr. Edward T. Chouchani & Dr. Haopeng Xiao of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute & Harvard Medical School and Dr. Diana C.F. Monteiro of the Hauptman-Woodward Medical Research Institute. I acknowledge financial support from start-up funds from the
 Structural insights into redox-active cysteine residues of the Src family kinases
Structural insights into redox-active cysteine residues of the Src family kinases