
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exist.
- Altmetric
Natural hybridization has been considered a source of taxonomic complexity in Cryptocoryne. A combined study of DNA sequencing data from the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) of nuclear ribosomal DNA and the trnK-matK region of chloroplast DNA was used to identify the parents of Cryptocoryne putative hybrids from Peninsular Malaysia. Based on the intermediate morphology and sympatric distribution area, the plants were tentatively identified as the hybrid Cryptocoryne ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea. The plants were pollen sterile and had long been considered as hybrids, supposedly between two related and co-existing species, C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii. The status of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea was independently confirmed by the presence of an additive ITS sequence pattern from these two parental species in hybrid individuals. An analysis of the chloroplast trnK-matK sequences showed that the hybridization is bidirectional with the putative hybrids sharing identical sequences from C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii, indicating that both putative parental species had been the maternal parent in different accessions.
Introduction
Natural interspecific hybridization has been demonstrated to be an important force in forming new species [1, 2] and plays a crucial role in plant evolution and diversification [3, 4]. The occurrence of natural hybridization between different species, however, is not universal but is concentrated among a limited fraction of plant families and genera [5]. Natural hybridization has been suggested to occur frequently in Cryptocoryne. The genus can be seen as having multiple populations in various river systems and hybridization can be an evolutionary driving force that constantly creates new genotypes that are spread across the ever-changing river systems [6–10]. Most recently, 65 species, 19 varieties and 15 named interspecific hybrids have been recognized [9–16]. Recognizing the Cryptocoryne hybrids began in the 1970s [17–19] and two of the Cryptocoryne hybrids have been recognized (as species) for more than 100 years. However, not until after 1975 was it realized and accepted that some of the plants were probably interspecific hybrids [17]. The uncertain status and tendency of Cryptocoryne to hybridize naturally may create more complexity in terms of taxonomic studies and classification. The natural Cryptocoryne hybrids have previously been reported in Peninsular Malaysia [6, 10, 17], Sri Lanka [19–21], Thailand and Lao P. D. R. [7, 18], Singapore [22], Sarawak [23], Kalimantan [14, 15, 24, 25] and Sumatera [13], with an overview presented by Jacobsen et al. [7]. Even though Cryptocoryne hybrids have greatly reduced fertility, the hybrids are highly successful due to the proliferous propagation by numerous, long, subterranean stolons, resulting in very large stands of hybrid plants, easily detectable in nature.
Cryptocoryne ×purpurea Ridl. nothovar. purpurea is a natural interspecific hybrid, which can be found in Peninsular Malaysia. Another natural interspecific hybrid, C. ×purpurea northovar. borneoensis can only be found in Borneo [24]. This Borneo hybrid differs from the Peninsular Malaysia hybrid by having a limb with a pronounced collar, a purple zone in the upper part of the kettle and a purple coloured appendix of the spadix. Additionally, the Bornean hybrid has a different chromosome number from the hybrid in Peninsular Malaysia and the former was suggested to have slightly different putative parents than the hybrid present in Peninsular Malaysia. According to Othman et al. [6], Cryptocoryne ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea was first collected from Kota Tinggi, Johor by Ridley in 1892, was cultivated in the Botanical Garden in Singapore and was shipped to Europe in 1898. It flowered at Kew and was pictured as C. griffithii Schott in the Botanical Magazine in 1900 (t 7719). In 1904, Ridley described this plant as a new species, named as C. purpurea. It was cultivated widely as an aquarium plant in Europe in the following years, although it almost disappeared towards the end of the century.
Based on the low pollen fertility [17], it was suggested that C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea was a hybrid of C. cordata Griff. var. cordata and C. griffithii Schott based on the coherence of morphological characteristics (broad collar zone–C. cordata var. cordata, and purple, rough spathe limb–C. griffithii) [6]. de Wit [26] gave a comprehensive explanation of the differences between C. griffithii, C. cordata var. cordata and C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea. Evidence of this morphological assumption gained support over the years and it is now generally accepted as a hybrid between the diploid C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii; moreover, both parents and the putative hybrid are found in the same region [6, 7].
Several molecular studies on the genus have been performed. One of the first molecular works focused on the phylogenetics of the genus, using nuclear and chloroplast DNAs [27]. The phylogeny of nuclear DNA suggests that C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea is closely associated with C. cordata var. cordata in contrast with the chloroplast DNA phylogeny, placing C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea in close association with C. griffithii. Although only one individual for each species was used, the results suggest that C. griffithii is the putative maternal parent and C. cordata var. cordata is the other putative parent in the studied material. In another study, random markers were used in the genetic studies of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea from locations in the Tasik Bera (Bera Lake) system in Peninsular Malaysia which indicated the presence of two distinct genetic groups, suggesting that two independent hybridization events or bidirectional hybridization had taken place [28]. Ipor et al. [29] used random markers to genotype the different C. ×purpurea hybrids from Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak and southern Kalimantan. Although the samples from Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo are treated as C. ×purpurea in a broad sense, their genetic results clearly separate the plants from Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo into two distinct clusters, supporting their different origins, i.e., C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea, 2n = 34 (C. cordata var. cordata, 2n = 34 × C. griffithii, 2n = 34) [17, 30], C. ×purpurea nothovar. borneoensis, 2n = 51 (C. cordata var. grabowskii (Engl.) N. Jacobsen, 2n = 68 × C. griffithii, 2n = 34) from southern Kalimantan [24]; the plants from Sungai Stungkor, Lundu, Sarawak, were later described as a separate pentaploid hybrid C. ×batangkayanensis Ipor et al. [23] with 2n = 85 between C. cordata var. grabowskii (2n = 68. unreduced) and C. ferruginea Engl. var. ferruginea (2n = 34) [23].
In a study on artificial hybridization between species of Cryptocoryne from Peninsular Malaysia, evidence indicated that C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea was a natural hybrid between C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii [8]. Verifying the hybrid origins of taxa in question is valuable in terms of studies on taxonomy, evolution and conservation. If parental species overlap at multiple locations across the geographical distribution, hybrids may emerge independently from hybridization of local parental genotype populations and may exhibit obvious morphological differences [31]. Therefore, different hybrid taxa with a slight morphological dissimilarity may have evolved as a result of hybridization of the same parental species at separate locations. In the present study, we compared two diverse C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea populations in streams only 2–3 km apart, which differed in shape, surface structure and colour of the spathe limb, representing two hybridization events with different parental genotypes in the state of Malacca [7]. Inferring the origins of such hybrid taxa based on morphology alone may, therefore, be difficult because morphologically similar hybrids can arise from the hybridization of different populations of the same parental species or be influenced by environmental conditions, which can be unreliable and misleading. In such cases, molecular means have been proven successful in identifying hybrid genotypes and determining the origins of various hybrid taxa [31–34].
Combined nuclear and plastid DNA markers provide potentially complementary evidence relating to a putative hybrid, allowing various questions to be investigated. To verify the hybrid origin of these intermediate individuals in the present study, a nuclear ribosomal DNA (nrDNA) internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region was first applied to examine the interspecific divergence between the putative parental species and assess the hybrid origin of the intermediate individuals by the additive patterns of both parental species. Secondly, the chloroplast trnK-matK region was applied due to its success in evaluating interspecific variation in most angiosperms, and also its use in identifying the maternal origin of hybrids.
Materials and methods
Plant material
The individuals of the putative hybrid C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea and the presumed parental species C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii were collected from different locations, in order to detect the potential intraspecific sequence of polymorphism. The permission for field work was granted by the Forestry Department of Peninsular Malaysia. The Department of Orang Asli Development, Malaysia, have given sampling authorization to reach several locations in Tasik Bera. We sampled seven individuals of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea, five individuals of C. cordata var. cordata and five individuals of C. griffithii respectively. For C. griffithii voucher number NJS 04–21, was presented to N. Jacobsen by Singapore Botanical Garden, from material grown in the garden while voucher number NJI 01–14 and NJS 04–21 were presented to N. Jacobsen by Oriental Aquarium, Singapore, Pte Ltd., from their nursery material. Since interspecific hybridization may be confounded by incomplete lineage sorting among closely related species, an additional Cryptocoryne species (C. nurii Furt. var. nurii and C. schulzei De Wit) was further examined. In addition, C. nurii var. nurii and C. schulzei were included in this study as their distribution was within the areas where the putative hybrids and presumed parental species are found. All accessions are summarized in Table 1.

| Taxon | Locality | Voucher and collection number | List of abbreviations |
|---|---|---|---|
| C. ×purpurea Ridl. nothovar. purpurea | Kampung Pulau Semut, Masjid Tanah, Malacca a | RR 11–06 | MT |
| Sungai Udang Recreational Forest, Malacca a | RR 12–02 | SU | |
| Pos Iskandar, Tasik Bera, Pahang a | RR 13–07 | PI | |
| Kampung Jelawat, Tasik Bera, Pahang a | RR 13–08 | KJ | |
| Paya Kelantong, Tasik Bera, Pahang a | RR 13–09 | PK | |
| Sungai Sedili Kechil, Kota Tinggi, Johor a | RR 11–10 | SED | |
| Kampung Sri Lukut, Kahang, Johor a | RR 12–04 | SL | |
| C. cordata Griff. var. cordata | Gunung Arong, Mersing, Johora | RR 12–05 | GA |
| Panti Bird Sanctuary, Kota Tinggi, Johor a | RR 11–07 | PAN | |
| Muadzam Shah, Pahang a | RR 11–24 | MU | |
| Sungai Tembangau, Tasik Bera, Pahanga | RR 10–03 | ST | |
| Bukit Sedanan, Masjid Tanah, Malacca a | RR 11–03 | BS | |
| C. griffithii Schott | Felda Nitar, Mersing, Johora | RR 15–01 | GF |
| Kulai, Johor a | NJM 01–3 | KUL | |
| Bintan b | NJI 01–14 | BIN | |
| Singapore Botanical Garden c | NJS 04–21 | BOT | |
| Singapore (Oriental Aquarium) c | NJS 01–16 | SIN | |
| C. nurii Furtado var. nurii | Kahang-Jemaluang, Mersing, Johor a | RR 11–16 | NKJ |
| Sungai Kahang, Johor a | RR 15–03 | NSK | |
| C. schulzei De Wit | Hutan Lipur Panti, Kota Tinggi, Johor a | RR 11–21 | SPAN |
| Kahang-Jemaluang, Mersing, Johor a | RR 11–17 | SKJ |
The latitude/longitude coordinates of the collection sites are not provided to ensure the protection of the species. RR are Rusly Rosazlina numbers and NJ are Niels Jacobsen numbers, deposited at USM. The first number after the initials represents the collection year and the second number is the running number.
a Malaysia
b Indonesia
c Singapore.
Fig 1 shows the spathe limbs of different accessions of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea and the putative parental species. RR voucher specimens have been deposited in the Herbarium Unit, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Penang (USMP) and NJ voucher specimens (and duplicates of most of the RR specimens) at the Botanical Museum, Copenhagen (C) (Natural History Museum of Denmark). Young leaves were cleaned with sterile distilled water before drying with silica gel. Upon completion of the drying process, samples were stored at -20°C before being used for DNA extraction.
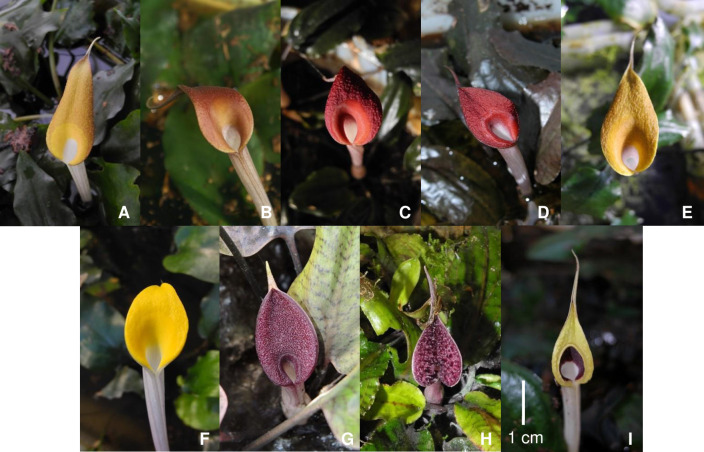


The spathe limbs of different accessions of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea and the putative parental species.
C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea (A, MT; B, SU; C, PI; D, SL; E, SED). C. cordata var. cordata (F, BS). C. griffithii (G, GF). C. nurii var. nurii (H, NSK). C. schulzei (I, SPAN). For the locality abbreviations, see Table 1.
DNA extraction, PCR amplification and sequencing
The total genomic DNA was extracted from silica-dried leaf tissue using the CTAB protocol described by Doyle and Doyle [35]. The nrDNA ITS and cpDNA trnK-matK regions were amplified using universal ITS1 and ITS4 primers [36] and trnK-3914F, trnK-2R primers [37] respectively. We obtained two newly designed primers for the trnK-matK regions specifically for the Cryptocoryne species; matKC-450F (5’-AGGGCAGAGTAGAGATGGATG-3’) and matKC-537R (5’-TATCAGAATCCGGCAAATCG-3’). The PCR products were directly sequenced using PCR primers after purification with Gel Clean-up System (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA). All sequencing reactions were carried out using the ABI 3700 DNA automated sequencer with the BigDye chemistry (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The ITS PCR products which produced unreadable sequence data with superimposed peaks in the chromatograms, were further purified using the Wizard SV DNA Clean-Up System (Promega Corp., Madison, WI, USA) and then cloned to ensure representative amplification of the parental copies using the pGEM-T Easy-cloning Vector Kit (Promega Corp., Madison, WI, USA) and transformed into competent Escherichia coli JM109 at 42°C. The transformed bacteria were screened on solid LB media with 100 mg/mL ampicillin at 37°C overnight. The six positive clones with the correct size inserts were confirmed using colony PCR and subsequently sequenced using the ITS primers described previously. The possibility of artificial recombinants being produced under standard PCR conditions was also tested using ITS primers and a 1:1 mixture of C. cordata var. cordata (GA) and C. griffithii (KUL) DNA as a template. All of the sequences were deposited in GenBank with accession numbers KU196170-KU196197 and KU196237-KU196248.
Sequence alignment and phylogenetic analyses
DNA sequences were assembled and aligned using (MEGA) 7.0 [38]. A most parsimonious (MP) unrooted tree was first built for ITS sequences of parents using PAUP* [39]. For this purpose, we conducted a heuristic search with starting trees obtained via stepwise addition with 100 iterations of the random addition sequence and the TBR branch-swapping option in PAUP*. All constants and variable (i.e., non-informative) characters were deleted. Only informative characters for parsimony were examined. The consistency index (CI) and the retention index (RI) were calculated, and the number of character changes were mapped on branches. Then, for each putative hybrid, we built an MP unrooted tree by combining its sequences with those of parents, using the same method of reconstruction and only parsimony-informative characters. Finally, an MP phylogenetic tree was built for all trnK-matK sequences of putative hybrids, C. cordata var. cordata, C. griffithii, and for C. nurii var. nurii and C. schulzei as outgroups.
Results
Sequence analysis of the nrITS region
The nuclear ITS sequences had a total aligned length of 736 bp with 12 fixed nucleotide substitutions and indels indicated, which distinguished the C. cordata var. cordata sequences from the C. griffithii sequences at species level (Table 2). All fixed nucleotide substitutions with all clone accession numbers were summarized in S1 Table. In the case of the putative hybrid, all individuals exhibited chromatogram peak additivity at all these fixed sites. No intraspecific polymorphism was detected within each putative parental species. Among the 42 cloned sequences of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea, 14 haplotypes (H1) were identical to C. griffithii; six haplotypes (H2) were identical to C. cordata var. cordata, and the remaining 22 cloned sequences (H3–H7) showed intermediate sequences between C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii. Of the six cloned sequences from the C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii template mixture, one was pure C. griffithii (H1), one was pure C. cordata var. cordata (H2), and the remaining four revealed intermediate sequences (H3). On the other hand, C. nurii var. nurii had ITS sequences different from those of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea at six positions, which eliminated C. nurii var. nurii as a possible parent. However, C. schulzei had identical ITS profiles to those of C. cordata var. cordata and C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea. This additivity strongly supports the fact that C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea is the hybrid of C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii, although ITS data alone cannot reject the possibility of it being C. griffithii × C. schulzei.

| Taxon | ITS Variable sites | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | ||
| 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 8 | ||
| 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 9 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 8 | 8 | ||
| C. griffithii | C | T | A | A | G | A | G | A | T | C | T | C | A | A | C | − | − | T | |
| C. cordata var. cordata | T | − | G | A | G | A | T | G | C | T | C | C | A | G | C | G | C | C | |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea | H1 (14) | C | T | A | A | G | A | G | A | T | C | T | C | A | A | C | − | − | T |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea | H2 (6) | T | − | G | A | G | A | T | G | C | T | C | C | A | G | C | G | C | C |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea | H3 (15) | C | T | G | A | G | A | T | G | C | T | C | C | A | G | C | G | C | C |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea | H4 (4) | C | T | G | A | G | A | T | G | C | T | C | C | A | G | C | − | − | C |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea | H5 (1) | C | T | A | A | G | A | G | A | T | T | T | C | A | G | C | − | − | T |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea | H6 (1) | C | T | G | A | G | A | T | G | C | T | C | C | A | G | C | − | C | C |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea | H7 (1) | T | − | G | A | G | A | T | G | C | T | C | C | A | G | C | − | − | C |
| DNA mixture | H1 (1) | C | T | A | A | G | A | G | A | T | C | T | C | A | A | C | − | − | T |
| DNA mixture | H2 (1) | T | − | G | A | G | A | T | G | C | T | C | C | A | G | C | G | C | C |
| DNA mixture | H3 (4) | C | T | G | A | G | A | T | G | C | T | C | C | A | G | C | G | C | C |
| C. schulzei | T | − | G | A | G | A | T | G | C | T | C | C | A | G | C | G | C | C | |
| C. nurii var. nurii | C | T | A | G | C | G | G | A | T | C | T | A | G | A | G | − | − | T | |
The numbers represent the positions of the variable sites. Seven haplotypes (H1-H7) with individual numbers are found in C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea. The DNA mixture of C. griffithii; KUL and C. cordata var. cordata; GA. “−” denotes a gap.
MP analysis based on equal weighting of each character, yielded one tree of 12 steps, with a CI of 1 and RI of 1. Fig 2A shows this tree in which the two putative parents, C. griffithii and C. cordata var. cordata, form two distinct groups that differ from one other by nine unique substitutions (= fixed differences). An analysis of the putative clonal hybrid sequences showed that of the four putative hybrids (PK, MT, KJ and SL), we identified two groups of sequences corresponding to C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii. These two groups differed from one other by six to eight unique substitutions. For putative hybrids PI, SED and SU, only sequences similar to C. cordata var. cordata were detected from the six sequenced clones.

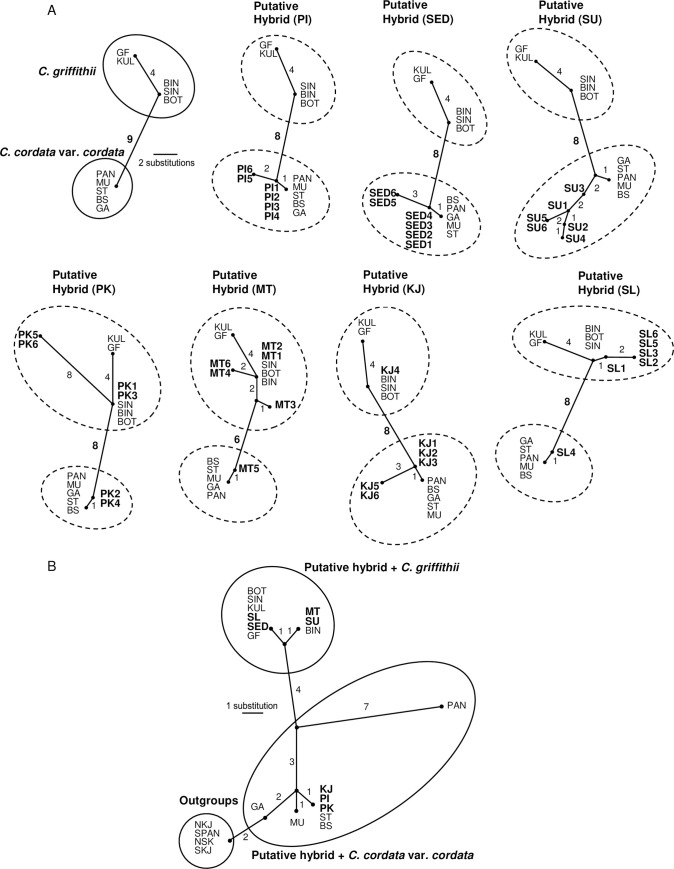
MP unrooted tree based on equal weighting of each character according to ITS (A) and trnK-matK (B) sequences. Clone accession numbers were included in the ITS tree as per the S1 Table. The numbers close to the connecting lines denote mutational steps.
Sequence analysis of the cpDNA region
The aligned length of the chloroplast trnK-matK region was 1980 bp across the whole dataset. An alignment of consensus nucleotide sequences from all samples varied at 20 sites (Table 3). In relation to these positions, four substitutions and six single-base pair indels distinguished the C. cordata var. cordata sequences from the C. griffithii sequences. No variation was identified in species sampled from the same location. The comparison showed that the putative hybrid samples from PI, KJ and PK had sequences identical to C. cordata var. cordata of ST and BS while SL and SED had sequences identical to C. griffithii (GF, KUL, BOT, SIN). The C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea accessions from MT and SU had sequences identical to C. griffithii (BIN) at one nucleotide position. The trnK-matK sequences of C. cordata var. cordata (PAN) differed by three substitutions and C. cordata var. cordata (GA) differed by two substitutions when compared to other C. cordata var. cordata accessions. The nucleotide composition for C. nurii var. nurii was identical to C. schulzei and dissimilar to that of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea at two nucleotide positions, rendering it unlikely that both C. nurii var. nurii and C. schulzei can be parents to C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea.

| Taxon | Variable sites | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 3 | 8 | |
| 8 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 9 | 9 | |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea; PI | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | T | T | G | T | T | T | T | G | A | T | T | C | T |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea; KJ | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | T | T | G | T | T | T | T | G | A | T | T | C | T |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea; PK | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | T | T | G | T | T | T | T | G | A | T | T | C | T |
| C. cordata var. cordata; ST | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | T | T | G | T | T | T | T | G | A | T | T | C | T |
| C. cordata var. cordata; BS | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | T | T | G | T | T | T | T | G | A | T | T | C | T |
| C. cordata var. cordata; MU | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | T | T | G | T | T | G | T | G | A | T | T | C | T |
| C. cordata var. cordata; GA | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | T | T | T | T | T | G | T | G | A | T | T | C | A |
| C. cordata var. cordata; PAN | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | T | T | G | C | T | G | T | A | A | G | T | C | T |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea; SL | G | C | T | G | T | A | T | T | G | G | C | T | G | G | A | G | G | C | A | T |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea; SED | G | C | T | G | T | A | T | T | G | G | C | T | G | G | A | G | G | C | A | T |
| C. griffithii; GF | G | C | T | G | T | A | T | T | G | G | C | T | G | G | A | G | G | C | A | T |
| C. griffithii; KUL | G | C | T | G | T | A | T | T | G | G | C | T | G | G | A | G | G | C | A | T |
| C. griffithii; BOT | G | C | T | G | T | A | T | T | G | G | C | T | G | G | A | G | G | C | A | T |
| C. griffithii; SIN | G | C | T | G | T | A | T | T | G | G | C | T | G | G | A | G | G | C | A | T |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea; MT | A | C | T | G | T | A | T | T | G | G | C | T | G | T | A | G | G | C | A | T |
| C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea; SU | A | C | T | G | T | A | T | T | G | G | C | T | G | T | A | G | G | C | A | T |
| C. griffithii; BIN | A | C | T | G | T | A | T | T | G | G | C | T | G | T | A | G | G | C | A | T |
| C. schulzei; SPAN | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | G | T | T | T | A | G | T | G | A | T | T | C | A |
| C. schulzei; SKJ | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | G | T | T | T | A | G | T | G | A | T | T | C | A |
| C. nurii var. nurii; NKJ | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | G | T | T | T | A | G | T | G | A | T | T | C | A |
| C. nurii var. nurii; NSK | G | − | − | − | − | − | − | G | T | T | T | A | G | T | G | A | T | T | C | A |
The numbers represent the positions of variable sites. “−” denotes a gap.
A phylogenetic analysis with the MP algorithm yielded one MP tree of 20 steps, with a CI of 1 and RI of 1. In this tree (Fig 2B), the ingroup and C. griffithii are each monophyletic, while C. cordata var. cordata is not monophyletic because outgroups are nested within. When the trnK-matK sequences of the putative hybrids are added to the dataset, the resulting MP tree shows that the maternal origin of the trnK-matK sequences of the putative hybrids KJ, PI and PK is C. cordata var. cordata, whereas C. griffithii is the parent of the trnK-matK sequences of the putative hybrids SL, SED, MT and SU.
Discussion
The nuclear genes are biparentally inherited, and the hybrids should possess both divergent copies of their putative parents [33, 34]. The nuclear ITS sequences of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea showed nucleotide polymorphism at some sites, whereas those of C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii did not (Table 2); the data from the C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea accessions exhibited polymorphism patterns which are consistently formed by additive sequences derived from two hypothesized parental species. The present ITS data revealed that C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea possessed hybrid genotypes, having both ITS haplotypes of parental C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii, therefore, suggesting that C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea is a natural hybrid of these two species. The results also showed that 22 (52.4%) out of the 42 cloned nrITS sequences from C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea were intermediate/chimeric (recombinations of parental sequence haplotypes (H3-H7)). In diploid hybrids, the co-occurrence of parental nrITS sequences is rarely maintained in subsequent generations due to concerted evolution; if concerted evolution is incomplete, then sampled genes may represent a mixture of non-homogenized paralogous sequences [40]. The effects of concerted evolution commonly occur after meiosis (sexual reproduction) but only in fertile plants [40–42]. However, Jacobsen [17] reported that the pollen of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea is completely sterile which was also the case in the samples being investigated. Cytological analysis shows that C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea shares the same diploid chromosome number 2n = 34 as C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii [17, 30], which rules out the possibility of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea being a sterile polyploid. Since C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea is sterile, all C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea individuals are assumed to represent an F1 generation. Therefore, F1 individuals should possess both parental ITS alleles without the impact of concerted evolution.
One explanation for the origin of such a unique allele in C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea may be the result of PCR-mediated recombination, a process of in vitro chimera formation from related DNA template sequences coamplified in a single PCR reaction [43]. PCR-mediated recombination results from either polymerase template switching during PCR or annealing of prematurely terminated products to non-homologous templates [43, 44]. This phenomenon has been well characterized from other hybrid plant species including Potamogeton intortusifolius [45], Malus toringoides [46] and Aster chusanensis [47]. In this study, the detection of chimeric haplotypes (H3) from an artificial DNA template (1:1 DNA mixture of C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii) may suggest that PCR-mediated recombination could be an explanation for the origin of chimeric nrITS PCR amplicons in C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea. Moreover, the chimeric haplotypes are unequally distributed in the nucleotide positions which indicates the process of recombination occurring in a non-random order during PCR. Techniques involving passing traditional PCR and cloning processes are necessary for further examination of the structure and evolution of nrITS sequences in C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea.
Due to the high sterility of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea, derived from the low pollen stainability with cotton blue [13], it may be inferred that sterility is also prevalent of the female side. However, we cannot rule out that a backcrossing from one of the putative parents may take place, but we have not observed any cases where that might have occurred in the present context, or perhaps our material is too limited to draw such conclusions. In other cases, regarding the Cryptocoryne species from Sri Lanka [21] second or more generations have been reported and assumed, but here the hybrids showed a certain degree of fertility. In C. crispatula Engl. s.l. from Mainland Asia, multiple hybrids have been observed and there is some fertility in the hybrids; backcrosses and introgressions are also suggested to be highly likely [7].
The results showed that the ITS sequences of C. cordata var. cordata and C. schulzei are very similar, suggesting that the C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea populations examined are hybrids of C. griffithii and either C. cordata var. cordata or C. schulzei. The hybrid has been found to grow sympatrically with C. griffithii and C. cordata var. cordata in Malacca and S.W. Johor, but also with C. schulzei in S.E. Johor. Cryptocoryne species are mainly identified using floral characters, particularly the limb of the spathe. Although the colours of the limb of the spathe of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea may vary, the surface structure shows intermediate characters between C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii, the broad collar zone being present in both C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea and C. cordata var. cordata and a rather rugose limb of the spathe, with a wide, pronounced collar is found in C. griffithii. C. schulzei does have a broad collar zone but has a strongly reflexed spathe limb [6]. A rough purple red limb of the spathe is characteristic of C. griffithii and resembles that of C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea; C. nurii var. nurii has a deep red to dark purple spathe with large irregular protuberances on the limb. In conclusion, with the joint examination of molecular and morphological datasets from the included accessions, it is unlikely that C. schulzei and C. nurii var. nurii are parents to C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea. In the aforementioned study on the artificial hybridization of species of Cryptocoryne from the Malay Peninsula, hybrids were produced between C. cordata var. cordata and C. nurii var. nurii which were unlike C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea [8]. Based on morphological characters, chromosome numbers and artificial hybridizations, two recent studies [9, 10] proposed that C. ×decus-silvae De Wit represents the hybrid C. cordata var. cordata × C. nurii var. nurii, C. ×griffithiioides N. Jacobsen represents the hybrid C. griffithii × C. nurii var. nurii and C. ×schulzeioides N. Jacobsen represents the hybrid C. griffithii × C. schulzei.
It is common to find more than one species of Cryptocoryne in southern Peninsular Malaysia (Pahang, Johor and Malacca) that share the same stream or river system. Suitable combinations of species coexist, resulting in hybridization conditions. The trnK-matK sequences of the C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea accessions PI, KJ and PK from Pahang (all originating from the Tasik Bera) were identical to C. cordata var. cordata and highlighted this species as the maternal parent (Table 3, Fig 2B). Neither putative parent was found in the hybrid sampling lake, but C. cordata var. cordata (ST) was present in the nearby swamp. The origin of the Tasik Bera area dates back to only 4500 years B.P. [48]. Based on the explanation of Othman et al. [6], the main drainage of the Tasik Bera is now northward to Sungai Pahang (Pahang River), but there is still a small connection southward to the Sungai Palong/Sungai Muar, Johor that was formally the main run-off. This historical evidence provides the explanation as to how C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea has arisen as a hybrid of the more widespread C. cordata var. cordata and the southerly distributed C. griffithii, which has then spread along the west coast during the change in drainage systems. The trnK-matK sequences of the C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea accessions from Johor (SL and SED) were identical to the C. griffithii populations from Johor (KUL and GF) and C. griffithii from Singapore (BOT and SIN). Currently it is known that the two putative parental species have both recently been found at the Sungai Sedili Kechil, Johor, and previous records have shown that C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii distribution overlapped in Johor [7, 49]. C. griffithii was also proposed as the maternal parent of the C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea populations from the Malacca region (MT and SU), viz. C. griffithii from BIN (Bintan, Indonesia). The other parental species C. cordata var. cordata (BS) were found within a distance of <40 km from all the hybrid locations in the Malacca region but C. griffithii has not been recorded in these locations recently. However, C. griffithii has previously been recorded as growing in several places in Malacca [6, 19]. The present results indicate that both C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii have served as the maternal donor and the different hybrid populations possess separate and independent origins. There was no distinct bias of maternal composition for either one of them and this suggests that natural hybridization between the two examined species is bidirectional.
The combined investigation of nuclear ribosomal DNA, viz. the ITS and the chloroplast DNA for the trnK-matK region, provide compelling evidence for the natural hybridization of C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii. Molecular data support the hypothesis that the morphologically intermediate plants are hybrids which share trnK-matK sequences identical to both C. cordata var. cordata and C. griffithii. As C. ×purpurea nothovar. purpurea is pollen sterile with the absence of meiotic recombination, the parental sequences of the nuclear and chloroplast markers may be retained in the vegetative progenies. This study provides substantial evidence for interspecific hybridizations in Cryptocoryne. It should be interesting to further investigate the population genetics, ploidy level and reproductive behaviour of the hybrids including the geographical distribution and the timing of hybridization events for a better understanding of the total extent of the hybridization process in Cryptocoryne.
Acknowledgements
Sebastien Lavoue and Siti Nurfazilah are thanked for their useful comments on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
References
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
 Molecular evidence of the hybrid origin of Cryptocoryne ×purpurea Ridl. nothovar. purpurea (Araceae)
Molecular evidence of the hybrid origin of Cryptocoryne ×purpurea Ridl. nothovar. purpurea (Araceae)
