
- Altmetric
Fig 1 in the original article [1] is incorrect. Fig 1 should have been individual figures, rather than one consolidated figure. The authors have provided correct versions of Fig 1 as new figures below. Figs 4–7 correspond with the originally published Fig 1. Please view Figs 4–7 here.

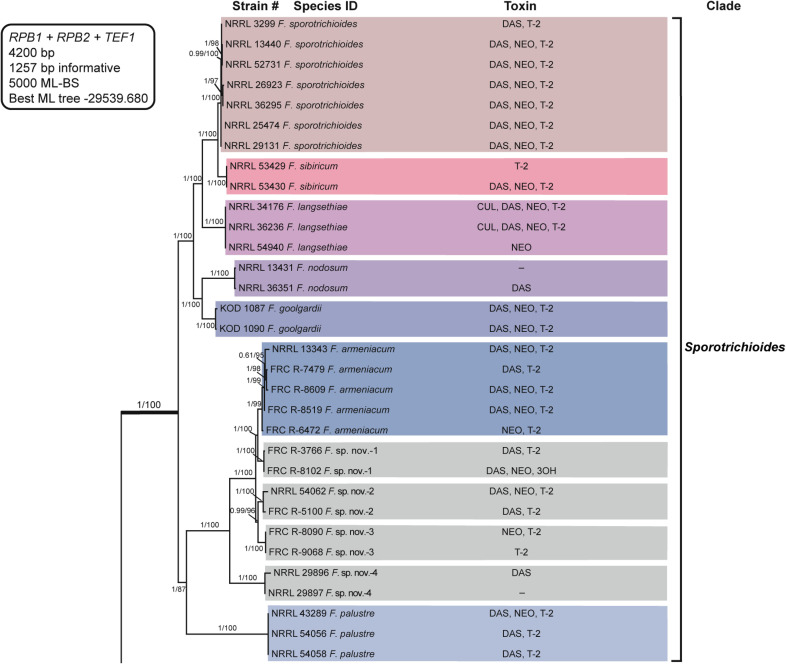
Fusarium sambucinum species complex. Bayesian and maximum likelihood phylogeny of the Sporotrichioides Clade inferred from partial RPB1 + RPB2 + TEF1 data set.
Support values above internodes are Bayesian posterior probabilities (BPP)/maximum likelihood bootstrap (ML-BS) values. BPP were calculated using MrBayes 3.2.7a [71]. ML-BS values were determined using IQ-TREE 1.6.12 [66]. The Sporotrichioides Clade (defined by thickened internode) was strongly supported as monophyletic (BPP = 1; ML-BS = 100%). Putatively novel species resolved within the Sporotrichioides Clade are designated F. sp. nov.-1 to -4. Toxins mapped on the phylogeny were determined via gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. CUL, culmorin; DAS, diacetoxyscirpenol; NEO, neosolaniol; T-2, T-2 toxin; 3OH, isotrichodermol;–, none detected.

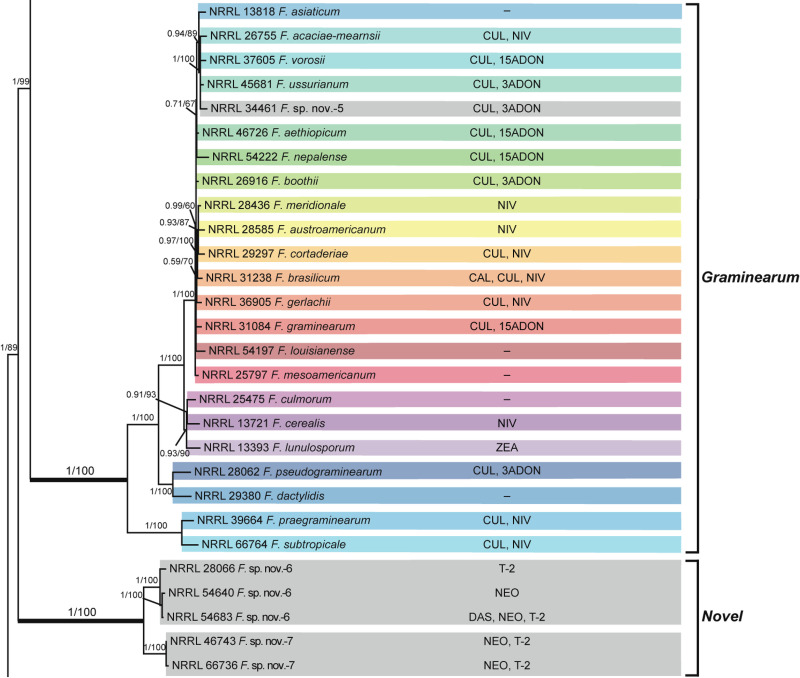
Fusarium sambucinum species complex. Bayesian and maximum likelihood phylogeny of the Graminearum and Novel Clades inferred from partial RPB1 + RPB2 + TEF1 data set.
Support values above internodes are Bayesian posterior probabilities (BPP)/maximum likelihood bootstrap (ML-BS) values. BPP were calculated using MrBayes 3.2.7a [71]. ML-BS values were determined using IQ-TREE 1.6.12 [66]. The Graminearum and Novel Clades (defined by thickened internodes) were strongly supported as monophyletic (BPP = 1; ML-BS = 100%). Putatively novel species resolved within the Graminearum and Novel Clades are designated F. sp. nov.-5 to -7. Toxins mapped on the phylogeny were determined via gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. CAL, calonectrin; CUL, culmorin; DAS, diacetoxyscirpenol; NEO, neosolaniol; NIV, nivalenol; T-2, T-2 toxin; ZEA, zearalenone; 3ADON, 3-acetyldeoxynivalenol; 15ADON, 15-acetyldeoxynivalenol;–, none detected.

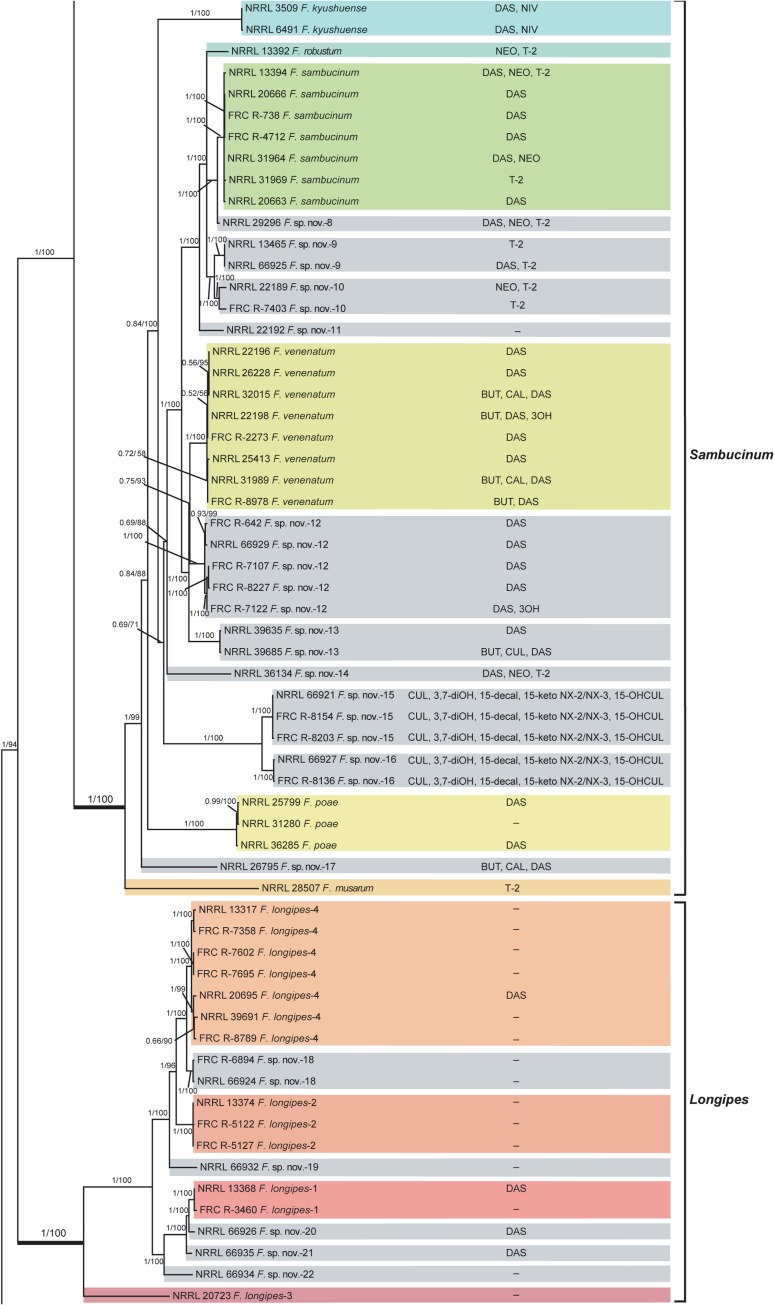
Fusarium sambucinum species complex. Bayesian and maximum likelihood phylogeny of the Sambucinum and Longipes Clades inferred from partial RPB1 + RPB2 + TEF1 data set.
Support values above internodes are Bayesian posterior probabilities (BPP)/maximum likelihood bootstrap (ML-BS) values. BPP were calculated using MrBayes 3.2.7a [71]. ML-BS values were determined using IQ-TREE 1.6.12 [66]. The Sambucinum and Longipes Clades (defined by thickened internodes) were strongly supported as monophyletic (BPP = 1; ML-BS = 100%). Putatively novel species resolved within the Sambucinum and Longipes clades are designated F. sp. nov.-8 to -22. Four phylogenetically distinct species within the Longipes Clade previously reported in other studies are identified by unique Arabic numbers (1 to 4). Toxins mapped on the phylogeny were determined via gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. BUT, butenolide; CAL, calonectrin; CUL, culmorin; DAS, diacetoxyscirpenol; NEO, neosolaniol; NIV, nivalenol; T-2, T-2 toxin; 3OH, isotrichodermol; 3,7-diOH, 7-hydroxy isotrichodermol; 15-decal, 15-decalonectrin; 15-keto NX-2 and 15-keto NX-3, novel type A trichothecenes; 15-OHCUL, 15-hydroxy culmorin;–, none detected.

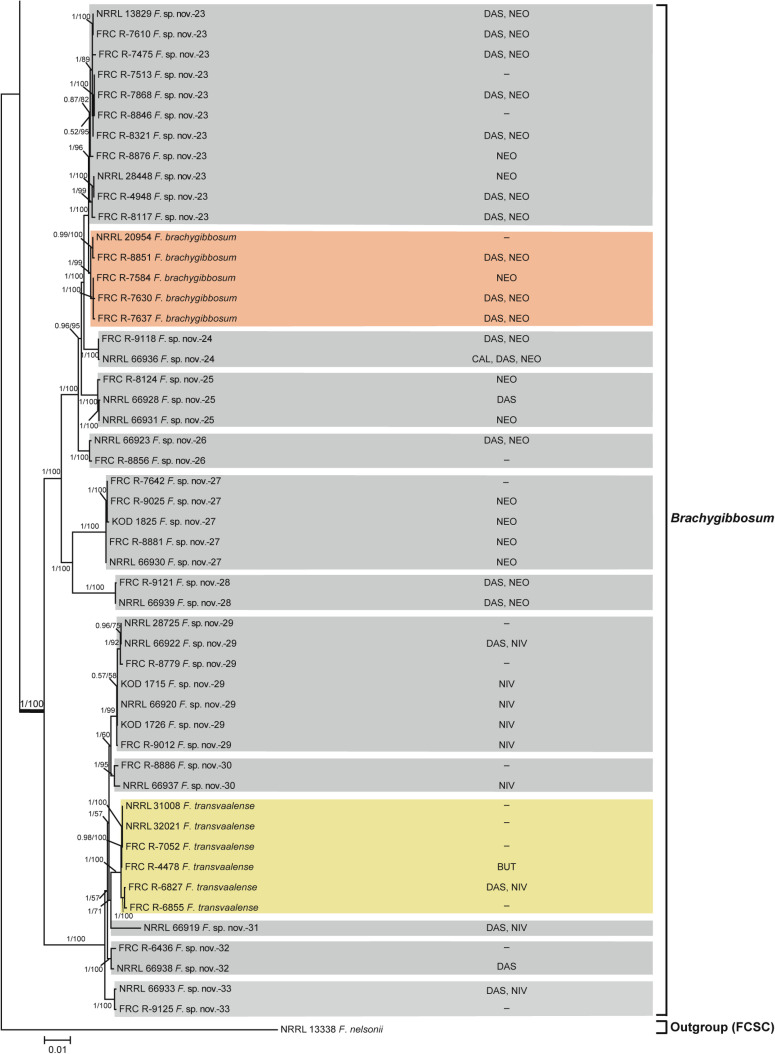
Fusarium sambucinum species complex.
Bayesian and maximum likelihood phylogeny of the Brachygibbosum Clade inferred from partial RPB1 + RPB2 + TEF1 data set. Support values above internodes are Bayesian posterior probabilities (BPP)/maximum likelihood bootstrap (ML-BS) values. BPP were calculated using MrBayes 3.2.7a [71]. ML-BS values were determined using IQ-TREE 1.6.12 [66]. The ingroup Fusarium sambucinum species complex was rooted on sequences of NRRL 13338 F. nelsonii from its sister group, the F. chlamydosporum species complex. The Brachygibbosum Clade (defined by thickened internode) was strongly supported as monophyletic (BPP = 1; ML-BS = 100%). Putatively novel species resolved within the Brachygibbosum Clade are designated F. sp. nov.-23 to -33. Toxins mapped on the phylogeny were determined via gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. BUT, butenolide; CAL, calonectrin; DAS, diacetoxyscirpenol; NEO, neosolaniol; NIV, nivalenol;–, none detected.
Reference
1
 Correction: Phylogenetic diversity, trichothecene potential, and pathogenicity within Fusarium sambucinum species complex
Correction: Phylogenetic diversity, trichothecene potential, and pathogenicity within Fusarium sambucinum species complex