PLoS ONE
Home
Correction: Investigation of the relationship between sensorineural hearing loss and associated comorbidities in patients with chronic kidney disease: A nationwide, population-based cohort study

Correction: Investigation of the relationship between sensorineural hearing loss and associated comorbidities in patients with chronic kidney disease: A nationwide, population-based cohort study
Article Type:
Correction
Article
History
Publisher:
Public Library of Science
- Altmetric
Table of Contents
The images for Figs 1 and 2 are incorrectly switched. The image that appears as Fig 1 should be Fig 2, and the image that appears as Fig 2 should be Fig 1. The figure captions appear in the correct order. The publisher apologizes for the error.

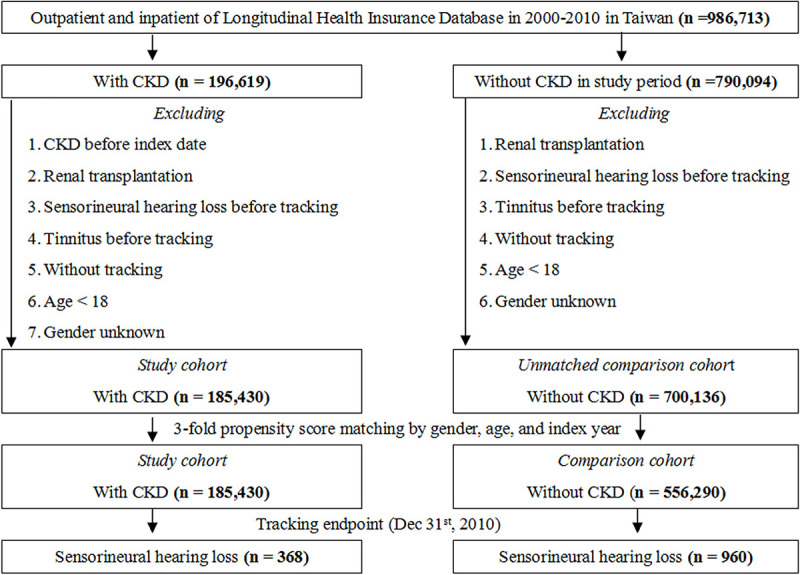
Fig 1
The flowchart of study sample selection.

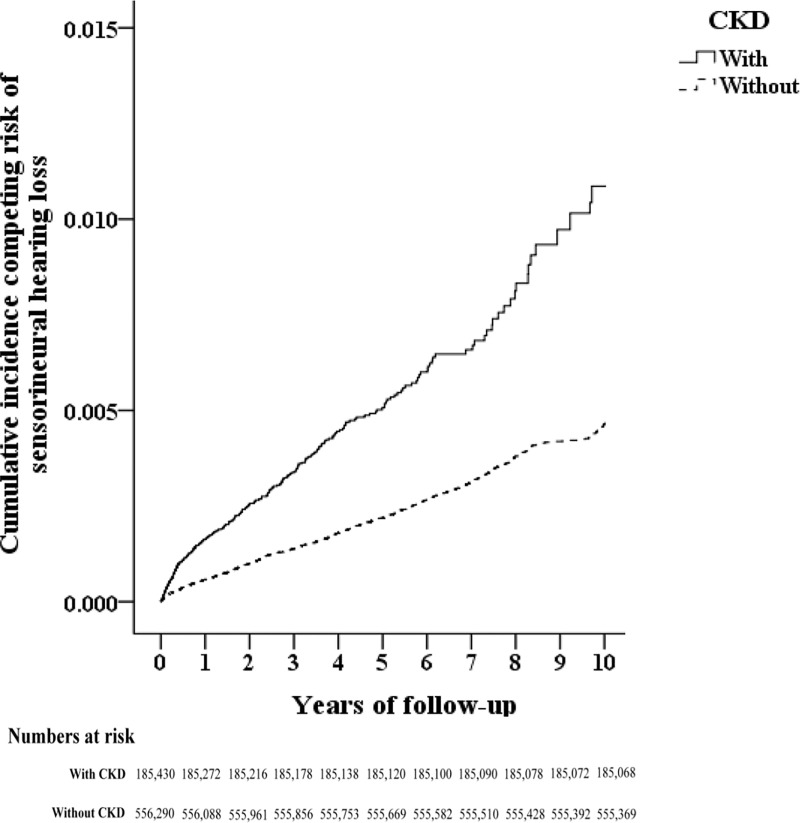
Fig 2
The cumulative incidence competing risk (CICR) method for the incidence of sensorineural hearing loss among patients aged 18 and over stratified by CKD (p < .001).
Reference
1
K-LWu, C-PShih, J-SChan, C-HChung, H-CLin, C-HTsao, et al (2020) Investigation of the relationship between sensorineural hearing loss and associated comorbidities in patients with chronic kidney disease: A nationwide, population-based cohort study. PLoS ONE
15(9): e0238913
10.1371/journal.pone.0238913
 Correction: Investigation of the relationship between sensorineural hearing loss and associated comorbidities in patients with chronic kidney disease: A nationwide, population-based cohort study
Correction: Investigation of the relationship between sensorineural hearing loss and associated comorbidities in patients with chronic kidney disease: A nationwide, population-based cohort study