PLoS ONE
Home
Correction: Fibromodulin-Deficiency Alters Temporospatial Expression Patterns of Transforming Growth Factor-β Ligands and Receptors during Adult Mouse Skin Wound Healing

Correction: Fibromodulin-Deficiency Alters Temporospatial Expression Patterns of Transforming Growth Factor-β Ligands and Receptors during Adult Mouse Skin Wound Healing
Article Type:
Correction
Article
History
Publisher:
Public Library of Science
- Altmetric
Table of Contents
In Fig 2E, the image labelled WT is a duplicate of Fig 2F. The authors have provided a corrected version here. The publisher apologizes for the error.

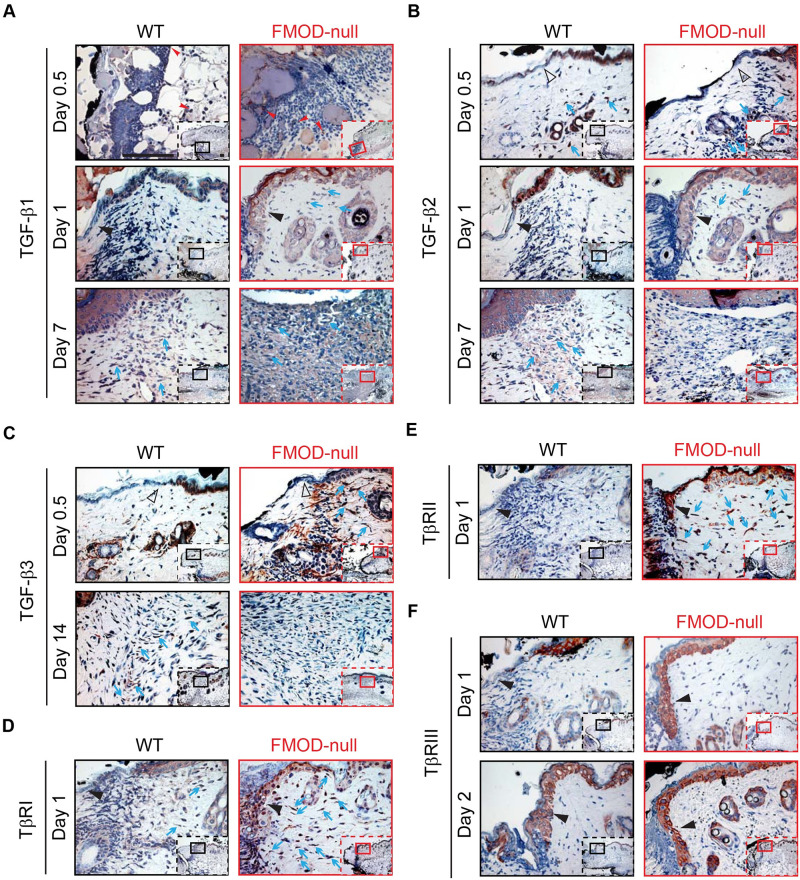
Fig 2
Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of wounded WT and FMOD-null adult mice skin.
(A) TGF-β1, (B) TGF-β2, (C) TGF-β3, (D) TβRI, (E) TβRII, and (F) TβRIII. Inserts show low magnification view. Red arrowheads: inflammatory cells; open black triangles: epidermis at wound edge; solid black triangles: migrating epidermal tongues; blue arrows: dermal fibroblasts. Bar = 100 μm.
Reference
1
ZZheng, KSLee, XZhang, CNguyen, CHsu, JZWang, et al (2014) Fibromodulin-Deficiency Alters Temporospatial Expression Patterns of Transforming Growth Factor-β Ligands and Receptors during Adult Mouse Skin Wound Healing. PLoS ONE
9(3): e90817
10.1371/journal.pone.0090817
 Correction: Fibromodulin-Deficiency Alters Temporospatial Expression Patterns of Transforming Growth Factor-β Ligands and Receptors during Adult Mouse Skin Wound Healing
Correction: Fibromodulin-Deficiency Alters Temporospatial Expression Patterns of Transforming Growth Factor-β Ligands and Receptors during Adult Mouse Skin Wound Healing