
Contributed equally.
To the editor:
Although acute kidney injury requiring kidney replacement therapy (AKI-KRT) is an important and severe complication in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), data on its long-term outcomes are currently limited. Previous studies reported that 65% to 70% of patients with AKI-KRT had recovered from dialysis dependency at the time of hospital discharge.1 , 2 However, long-term renal outcomes are unknown, because post-hospital follow-up after COVID-19–associated AKI in previous studies was limited to short observational periods.1 , 3 We retrospectively analyzed renal outcomes in 74 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and AKI-KRT in a large tertiary care center in Berlin, Germany, between March and June 2020. Patients were predominantly male (74.3%); the median age was 65 years; and the median baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate was 76.5 ml/min per 1.73 m2 (Supplementary Table S1). All patients were treated in intensive care units at the time of AKI-KRT onset; 98.6% of patients were mechanically ventilated, and 39.2% received extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy. COVID-19–specific therapies included corticosteroids (68%), hydroxychloroquine (4.1%), anakinra (8.1%), immunoglobulins (6.8%), tocilizumab (1.4%), and lopinavir-ritonavir (1.4%) (Supplementary Table S1). On October 21, 2020, after a median follow-up of 151 days (interquartile range 128–192 days) post-initiation of KRT, 36 patients (48.6%) had died during hospitalization, 1 patient (1.4%) was still hospitalized, and 37 (50%) had been discharged. In discharged survivors, the median overall duration of KRT was 27 days (interquartile range 11–50 days). At the end of follow-up, 3 patients (8.1%) were KRT-dependent while the remaining 34 patients (91.9%) had achieved variable degrees of renal recovery, including 23 patients (62.2%) with full renal recovery (Figure 1 ; Supplementary Table S1). These findings indicate that renal recovery is common in COVID-19 survivors even after long periods of KRT requirement during AKI. This information may be of value for patients with COVID-19 and their clinicians when it comes to deciding about the initiation or continuation of KRT.

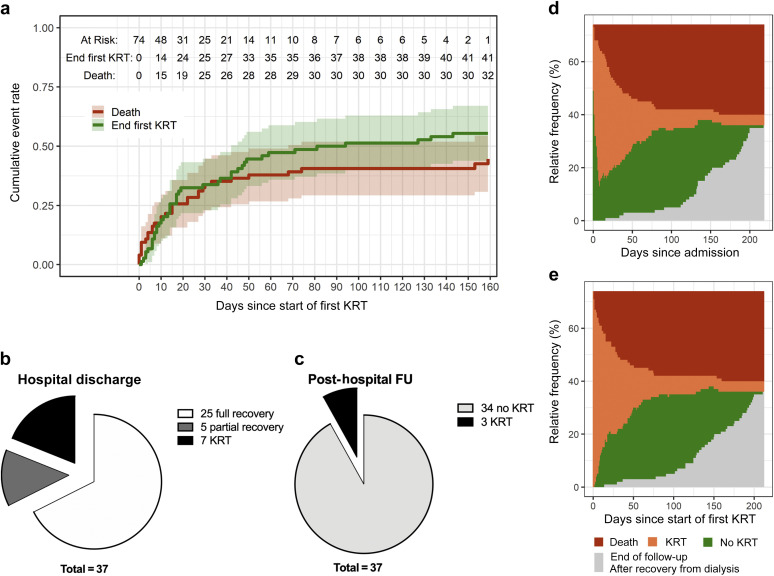
Renal outcomes after coronavirus disease 2019–associated acute kidney injury requiring kidney replacement therapy (KRT).(a) Cumulative incidence function for the end of first KRT, with death as a competing risk. (b) Renal outcome of discharged survivors at hospital discharge. (c) Renal outcome of discharged survivors at post-hospital follow-up (FU). (d,e) Course of dialysis dependency with daily patient data as stacked bar chart with (d) hospital admission or (e) start of KRT as the start date.
1
2
Table S1.: Patient characteristics and outcomes.